Page 1008 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1008
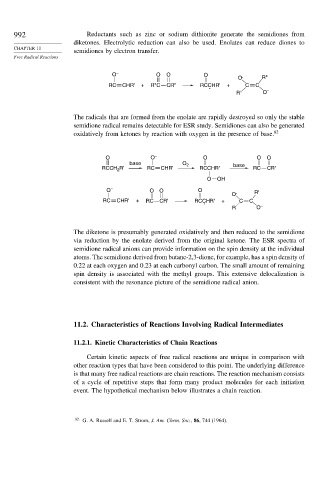
992 Reductants such as zinc or sodium dithionite generate the semidiones from
diketones. Electrolytic reduction can also be used. Enolates can reduce diones to
CHAPTER 11
semidiones by electron transfer.
Free Radical Reactions
O – O O O
O . R"
RC CHR' + R"C CR" RCCHR' + C C
.
R" O –
The radicals that are formed from the enolate are rapidly destroyed so only the stable
semidione radical remains detectable for ESR study. Semidiones can also be generated
oxidatively from ketones by reaction with oxygen in the presence of base. 82
O O – O O O
base O 2 base
RCCH R' RC CHR' RCCHR' RC CR'
2
O OH
O – O O O R'
O .
RC CHR' + RC CR' RCCHR' + C C
.
R O –
The diketone is presumably generated oxidatively and then reduced to the semidione
via reduction by the enolate derived from the original ketone. The ESR spectra of
semidione radical anions can provide information on the spin density at the individual
atoms. The semidione derived from butane-2,3-dione, for example, has a spin density of
0.22 at each oxygen and 0.23 at each carbonyl carbon. The small amount of remaining
spin density is associated with the methyl groups. This extensive delocalization is
consistent with the resonance picture of the semidione radical anion.
11.2. Characteristics of Reactions Involving Radical Intermediates
11.2.1. Kinetic Characteristics of Chain Reactions
Certain kinetic aspects of free radical reactions are unique in comparison with
other reaction types that have been considered to this point. The underlying difference
is that many free radical reactions are chain reactions. The reaction mechanism consists
of a cycle of repetitive steps that form many product molecules for each initiation
event. The hypothetical mechanism below illustrates a chain reaction.
82
G. A. Russell and E. T. Strom, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 86, 744 (1964).