Page 1017 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1017
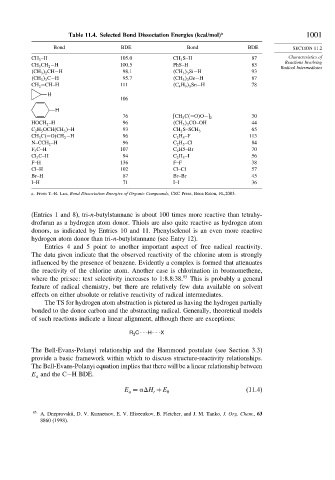
Table 11.4. Selected Bond Dissociation Energies (kcal/mol) a 1001
Bond BDE Bond BDE SECTION 11.2
CH 3 –H 105 0 CH 3 S–H 87 Characteristics of
Reactions Involving
CH 3 CH 2 −H 100 5 PhS–H 83
Radical Intermediates
CH 3
2 CH−H 98 1 CH 3
3 Si−H 93
CH 3
3 C−H 95 7 CH 3
3 Ge−H 87
CH 2 =CH–H 111 C 4 H 9
3 Sn−H 78
H
106
H
76 CH 3 C =O
O− 2 30
HOCH 2 –H 96 CH 3
3 CO–OH 44
C 2 H 5 OCH CH 3
–H 93 CH 3 S–SCH 3 65
CH 3 C =O
CH 2 −H 96 C 2 H 5 –F 113
N–CCH 2 –H 96 C 2 H 5 –Cl 84
F 3 C–H 107 C 2 H5–Br 70
Cl 3 C–H 94 C 2 H 5 –I 56
F–H 136 F–F 38
Cl–H 102 Cl–Cl 57
Br–H 87 Br–Br 45
I–H 71 I–I 36
a. From Y.-R. Luo, Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Compounds, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL,2003.
(Entries 1 and 8), tri-n-butylstannane is about 100 times more reactive than tetrahy-
drofuran as a hydrogen atom donor. Thiols are also quite reactive as hydrogen atom
donors, as indicated by Entries 10 and 11. Phenylselenol is an even more reactive
hydrogen atom donor than tri-n-butylstannane (see Entry 12).
Entries 4 and 5 point to another important aspect of free radical reactivity.
The data given indicate that the observed reactivity of the chlorine atom is strongly
influenced by the presence of benzene. Evidently a complex is formed that attenuates
the reactivity of the chlorine atom. Another case is chlorination in bromomethene,
where the pri:sec: text selectivity increases to 1:8.8:38. 85 This is probably a general
feature of radical chemistry, but there are relatively few data available on solvent
effects on either absolute or relative reactivity of radical intermediates.
The TS for hydrogen atom abstraction is pictured as having the hydrogen partially
bonded to the donor carbon and the abstracting radical. Generally, theoretical models
of such reactions indicate a linear alignment, although there are exceptions:
R C H X
3
The Bell-Evans-Polanyi relationship and the Hammond postulate (see Section 3.3)
provide a basic framework within which to discuss structure-reactivity relationships.
The Bell-Evans-Polanyi equation implies that there will be a linear relationship between
E and the C−H BDE.
a
E = H +E 0 (11.4)
r
a
85
A. Dneprovskii, D. V. Kuznetsov, E. V. Eliseenkov, B. Fletcher, and J. M. Tanko, J. Org. Chem., 63
8860 (1998).