Page 1141 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1141
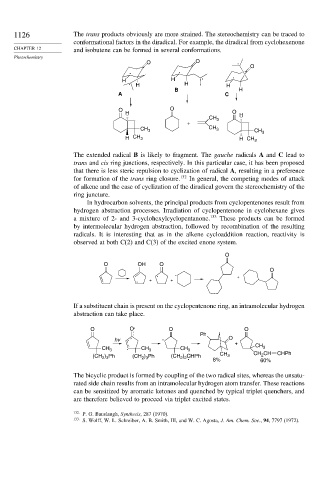
1126 The trans products obviously are more strained. The stereochemistry can be traced to
conformational factors in the diradical. For example, the diradical from cyclohexenone
CHAPTER 12 and isobutene can be formed in several conformations.
Photochemistry
O O .
O
. .
H H . .
. H H H
B H
A C
O O
H O
H
CH 3
+
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
H CH 3 H CH 3
The extended radical B is likely to fragment. The gauche radicals A and C lead to
trans and cis ring junctions, respectively. In this particular case, it has been proposed
that there is less steric repulsion to cyclization of radical A, resulting in a preference
for formation of the trans ring closure. 132 In general, the competing modes of attack
of alkene and the ease of cyclization of the diradical govern the stereochemistry of the
ring juncture.
In hydrocarbon solvents, the principal products from cyclopentenones result from
hydrogen abstraction processes. Irradiation of cyclopentenone in cyclohexane gives
a mixture of 2- and 3-cyclohexylcyclopentanone. 133 These products can be formed
by intermolecular hydrogen abstraction, followed by recombination of the resulting
radicals. It is interesting that as in the alkene cycloaddition reaction, reactivity is
observed at both C(2) and C(3) of the excited enone system.
O
O OH O
O
. . +
. + +
If a substituent chain is present on the cyclopentenone ring, an intramolecular hydrogen
abstraction can take place.
O O . O O
Ph
hv . O
+ CH
. CH CH 3
CH 3 3 3
CH CH CH CHPh
2
) Ph
(CH ) Ph (CH 2 3 (CH ) CHPh 8% 3 60%
.
2 3
2 2
The bicyclic product is formed by coupling of the two radical sites, whereas the unsatu-
rated side chain results from an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer. These reactions
can be sensitized by aromatic ketones and quenched by typical triplet quenchers, and
are therefore believed to proceed via triplet excited states.
132 P. G. Bauslaugh, Synthesis, 287 (1970).
133
S. Wolff, W. L. Schreiber, A. B. Smith, III, and W. C. Agosta, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 7797 (1972).