Page 842 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 842
9.2. Although N,N-dimethylaniline is extremely reactive toward electrophilic 825
aromatic substitution and is readily substituted by weak electrophiles, such
PROBLEMS
as diazonium and nitrosonium ions, this reactivity is greatly diminished by
introduction of an alkyl substituent in an ortho position. Explain.
9.3. Toluene is 28 times more reactive than benzene, whereas isopropylbenzene is
14 times more reactive than benzene toward nitration in the organic solvent
sulfolane. The o:m:p ratio for toluene is 62:3:35. For isopropylbenzene, the
ratio is 43:5:52. Calculate the partial rate factors for each position in toluene and
isopropylbenzene. Discuss the significance of the partial rate factors. Compare
the reactivity at each position of the molecules, and explain any significant
differences.
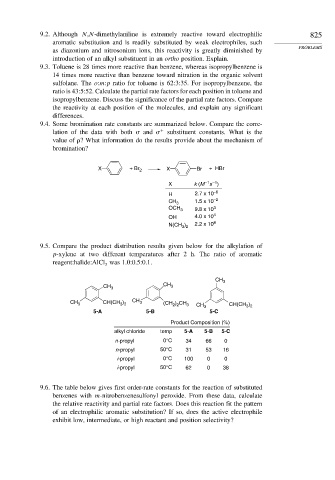
9.4. Some bromination rate constants are summarized below. Compare the corre-
lation of the data with both and + substituent constants. What is the
value of ? What information do the results provide about the mechanism of
bromination?
X + Br 2 X Br + HBr
–1 –1
X k (M s )
H 2.7 x 10 –6
1.5 x 10 –2
CH 3
OCH 3 9.8 x 10 3
OH 4.0 x 10 4
N(CH ) 2.2 x 10 8
3 2
9.5. Compare the product distribution results given below for the alkylation of
p-xylene at two different temperatures after 2 h. The ratio of aromatic
reagent:halide:AlCl was 1.0:0.5:0.1.
3
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
CH 3 CH(CH ) CH 3 (CH ) CH 3 CH 3 CH(CH )
3 2
2 2
3 2
5-A 5-B 5-C
Product Composition (%)
alkyl chloride temp 5-A 5-B 5-C
n-propyl 0°C 34 66 0
n-propyl 50°C 31 53 16
i-propyl 0°C 100 0 0
i-propyl 50°C 62 0 38
9.6. The table below gives first order-rate constants for the reaction of substituted
benzenes with m-nitrobenzenesulfonyl peroxide. From these data, calculate
the relative reactivity and partial rate factors. Does this reaction fit the pattern
of an electrophilic aromatic substitution? If so, does the active electrophile
exhibit low, intermediate, or high reactant and position selectivity?