Page 844 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 844
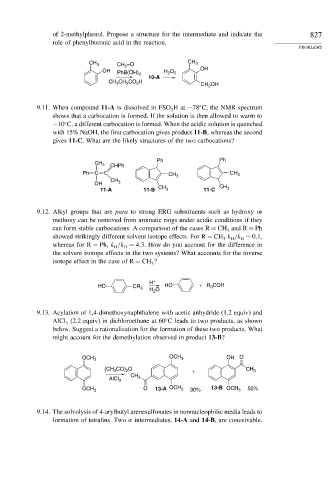
of 2-methylphenol. Propose a structure for the intermediate and indicate the 827
role of phenylboronic acid in the reaction.
PROBLEMS
CH 3 CH 2 =O CH 3
OH PhB(OH) H O 2 OH
2
2
10-A
CH CH CO H
2
2
3
CH 2 OH
9.11. When compound 11-A is dissolved in FSO Hat −78 C, the NMR spectrum
3
shows that a carbocation is formed. If the solution is then allowed to warm to
−10 C, a different carbocation is formed. When the acidic solution is quenched
with 15% NaOH, the first carbocation gives product 11-B, whereas the second
gives 11-C. What are the likely structures of the two carbocations?
Ph Ph
CH 3
CHPh
Ph C C CH 3 CH 3
OH CH 3 CH
11-A 11-B CH 3 11-C 3
9.12. Alkyl groups that are para to strong ERG substituents such as hydroxy or
methoxy can be removed from aromatic rings under acidic conditions if they
can form stable carbocations. A comparison of the cases R = CH and R = Ph
3
showed strikingly different solvent isotope effects. For R = CH k /k ∼ 0 1,
3
D
H
whereas for R = Ph, k /k = 4 3. How do you account for the difference in
D
H
the solvent isotope effects in the two systems? What accounts for the inverse
isotope effect in the case of R = CH ?
3
H +
HO CR 3 H O HO +R 3 COH
2
9.13. Acylation of 1,4-dimethoxynaphthalene with acetic anhydride (1.2 equiv) and
AlCl (2.2 equiv) in dichloroethane at 60 C leads to two products, as shown
3
below. Suggest a rationalization for the formation of these two products. What
might account for the demethylation observed in product 13-B?
OCH 3 OCH 3 OH O
(CH CO) O + CH 3
3
2
CH 3
AlCl 3
OCH 3 O 13-A OCH 3 30% 13-B OCH 3 50%
9.14. The solvolysis of 4-arylbutyl arenesulfonates in nonnucleophilic media leads to
formation of tetralins. Two intermediates, 14-A and 14-B, are conceivable.