Page 1024 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1024
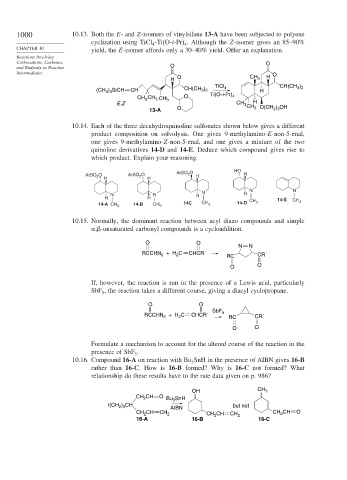
1000 10.13. Both the E- and Z-isomers of vinylsilane 13-A have been subjected to polyene
cyclization using TiCl -Ti(O-i-Pr) . Although the Z-isomer gives an 85–90%
4 4
CHAPTER 10 yield, the E-isomer affords only a 30–40% yield. Offer an explanation.
Reactions Involving
Carbocations, Carbenes, O
and Radicals as Reactive O
Intermediates O
O H
H CH 3
TiCl CH(CH )
3 2
)
(CH ) SiCH CH CH(CH 3 2 4 H
3 3
CH CH 3 CH 3 O Ti(O-i-Pr) 4
3
E,Z CH 3 CH H O(CH ) OH
13-A O 3 2 3
10.14. Each of the three decahydroquinoline sulfonates shown below gives a different
product composition on solvolysis. One gives 9-methylamino-E-non-5-enal,
one gives 9-methylamino-Z-non-5-enal, and one gives a mixture of the two
quinoline derivatives 14-D and 14-E. Deduce which compound gives rise to
which product. Explain your reasoning.
HO
ArSO 2 O
ArSO 2 O ArSO 2 O H H
H H
N N
N
N N H H
H H 14-E
14-A CH 3 14-B CH 3 14C CH 3 14-D CH 3 CH 3
10.15. Normally, the dominant reaction between acyl diazo compounds and simple
, -unsaturated carbonyl compounds is a cycloaddition.
O O
N N
+ H C CHCR´
RCCHN 2 2 RC CR´
O O
If, however, the reaction is run in the presence of a Lewis acid, particularly
SbF , the reaction takes a different course, giving a diacyl cyclopropane.
5
O O
SbF
RCCHN + H C CHCR´ 5 RC CR´
2
2
O O
Formulate a mechanism to account for the altered course of the reaction in the
presence of SbF .
5
10.16. Compound 16-A on reaction with Bu SnH in the presence of AIBN gives 16-B
3
rather than 16-C. How is 16-B formed? Why is 16-C not formed? What
relationship do these results have to the rate data given on p. 986?
OH CH 3
CH CH O Bu 3 SnH
2
I(CH ) CH AIBN but not
2 3
CH CH CH CH O
CH 2 2 CH CH CH 2 2
2
16-A 16-B 16-C