Page 1136 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1136
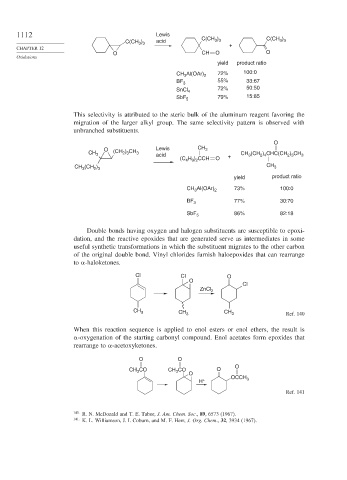
1112 Lewis C(CH )
3 3
C(CH ) acid 3 3 C(CH )
3 3
CHAPTER 12 +
O CH O O
Oxidations
yield product ratio
CH Al(OAr) 2 72% 100:0
3
BF 3 55% 33:67
SnCl 4 72% 50:50
SbF 5 79% 15:85
This selectivity is attributed to the steric bulk of the aluminum reagent favoring the
migration of the larger alkyl group. The same selectivity pattern is observed with
unbranched substituents.
O
O Lewis CH 3
CH 3 (CH ) CH 3 acid + CH (CH ) CHC(CH ) CH 3
2 3
2 3
2 4
3
H ) CCH
(C 4 9 2 O
CH (CH ) CH 3
3
2 3
yield product ratio
CH Al(OAr) 2 73% 100:0
3
BF 3 77% 30:70
SbF 5 86% 82:18
Double bonds having oxygen and halogen substituents are susceptible to epoxi-
dation, and the reactive epoxides that are generated serve as intermediates in some
useful synthetic transformations in which the substituent migrates to the other carbon
of the original double bond. Vinyl chlorides furnish haloepoxides that can rearrange
to -haloketones.
Cl Cl O
O
Cl
ZnCl 2
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Ref. 140
When this reaction sequence is applied to enol esters or enol ethers, the result is
-oxygenation of the starting carbonyl compound. Enol acetates form epoxides that
rearrange to -acetoxyketones.
O O
O
CH CO CH CO O
3
3
O
H + OCCH 3
Ref. 141
140 R. N. McDonald and T. E. Tabor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 89, 6573 (1967).
141
K. L. Williamson, J. I. Coburn, and M. F. Herr, J. Org. Chem., 32, 3934 (1967).