Page 1137 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1137
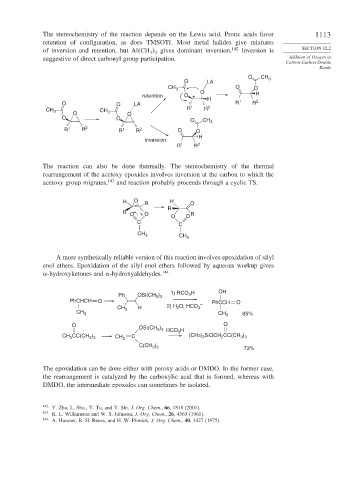
The stereochemistry of the reaction depends on the Lewis acid. Protic acids favor 1113
retention of configuration, as does TMSOTf. Most metal halides give mixtures
of inversion and retention, but Al CH gives dominant inversion. 142 Inversion is SECTION 12.2
3 3
suggestive of direct carbonyl group participation. Addition of Oxygen at
Carbon-Carbon Double
Bonds
O CH
O LA 3
CH 3 O O
O H
retention O +
H
O O LA 1 2 R 1 R 2
CH 3 CH 3 R R
O O
O O O CH 3
R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 O O
H
inversion
R 1 R 2
The reaction can also be done thermally. The stereochemistry of the thermal
rearrangement of the acetoxy epoxides involves inversion at the carbon to which the
acetoxy group migrates, 143 and reaction probably proceeds through a cyclic TS.
H O R H O
R
R O O R
O O
C C
CH 3
CH 3
A more synthetically reliable version of this reaction involves epoxidation of silyl
enol ethers. Epoxidation of the silyl enol ethers followed by aqueous workup gives
-hydroxyketones and -hydroxyaldehydes. 144
)
3
Ph OSi(CH 3 3 1) RCO H OH
PhCHCH O – PhCCH O
CH 3 H 2) H 2 O, HCO 3
CH 3 CH 3 85%
O OSi(CH ) RCO H O
3 3
CH CC(CH ) CH 2 C 3 (CH3) SiOCH CC(CH )
3 3
2
3
3 3
3
C(CH ) 73%
3 3
The epoxidation can be done either with peroxy acids or DMDO. In the former case,
the rearrangement is catalyzed by the carboxylic acid that is formed, whereas with
DMDO, the intermediate epoxides can sometimes be isolated.
142
Y. Zhu, L. Shu., Y. Tu, and Y. Shi, J. Org. Chem., 66, 1818 (2001).
143 K. L. Williamson and W. S. Johnson, J. Org. Chem., 26, 4563 (1961).
144
A. Hassner, R. H. Reuss, and H. W. Pinnick, J. Org. Chem., 40, 3427 (1975).