Page 1177 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1177
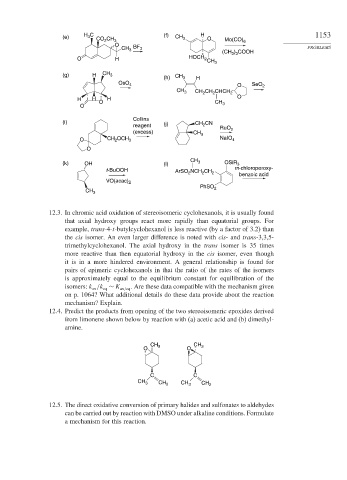
(e) H C CO CH 3 (f) CH 3 H O Mo(CO) 6 1153
3
2
O
CH BF 3 PROBLEMS
3
(CH 3 ) 3 COOH
O H HOCH 2 CH 3
(g) H CH 3 CH
(h) 3 H
OsO 4 O SeO 2
CH 3 CH CH CHCH 2
2
2
H H H O
O CH 3
O
Collins
(i) CH CN
reagent (j) 2
RuO 2
(excess) CH 3
O CH 2 OCH 3 NaIO 4
O
CH
(k) OH (l) 3 OSiR 3
t-BuOOH ArSO 2 NCH 2 CH 2 m-chloroperoxy-
benzoic acid
VO(acac) 2
PhSO 2
CH 3
12.3. In chromic acid oxidation of stereoisomeric cyclohexanols, it is usually found
that axial hydroxy groups react more rapidly than equatorial groups. For
example, trans-4-t-butylcyclohexanol is less reactive (by a factor of 3.2) than
the cis isomer. An even larger difference is noted with cis- and trans-3,3,5-
trimethylcyclohexanol. The axial hydroxy in the trans isomer is 35 times
more reactive than then equatorial hydroxy in the cis isomer, even though
it is in a more hindered environment. A general relationship is found for
pairs of epimeric cyclohexanols in that the ratio of the rates of the isomers
is approximately equal to the equilibrium constant for equilibration of the
isomers: k /k ∼ K ax/eq . Are these data compatible with the mechanism given
eq
ax
on p. 1064? What additional details do these data provide about the reaction
mechanism? Explain.
12.4. Predict the products from opening of the two stereoisomeric epoxides derived
from limonene shown below by reaction with (a) acetic acid and (b) dimethyl-
amine.
CH 3 CH 3
O O
C C
CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH 2
12.5. The direct oxidative conversion of primary halides and sulfonates to aldehydes
can be carried out by reaction with DMSO under alkaline conditions. Formulate
a mechanism for this reaction.