Page 626 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 626
600 The minimum-energy TSs are planar and the O−H and C−H bond orders were usually
less than 0.4 and less than 0.5, respectively, and the S−C bond order was less than 0.5.
CHAPTER 6
The C−C bond order was around 1.3. The reaction can be described as a concerted
Concerted intramolecular proton transfer, with the sulfoxide oxygen acting as a base and the
Cycloadditions,
Unimolecular sulfur as a leaving group.
Rearrangements, and
Thermal Eliminations
O – H
S + CHR
R′
H H
The TS for selenoxide elimination has also been examined computationally. 334 The
C−H bond cleavage runs ahead of the C−Se cleavage.
A third category of syn eliminations involves pyrolytic decomposition of esters
with elimination of a carboxylic acid. The pyrolysis of acetate esters normally requires
temperatures above 400 C and is usually a vapor phase reaction. In the laboratory this
is done by using a glass tube in the heating zone of a small furnace. The vapors of
the reactant are swept through the hot chamber by an inert gas and into a cold trap.
Similar reactions occur with esters derived from long-chain acids. If the boiling point
of the ester is above the decomposition temperature, the reaction can be carried out in
the liquid phase, with distillation of the pyrolysis product.
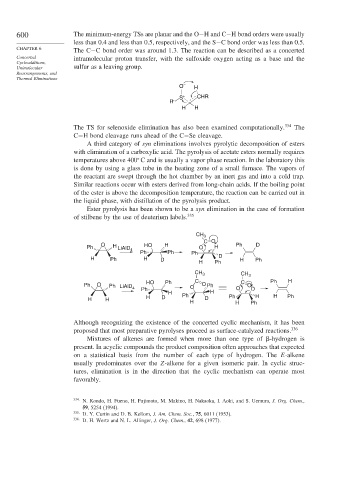
Ester pyrolysis has been shown to be a syn elimination in the case of formation
of stilbene by the use of deuterium labels. 335
CH 3
C O
O HO H Ph D
Ph H LiAlD 4 O H
Ph Ph Ph
H Ph H D D H Ph
H Ph
CH 3 CH 3
HO Ph C C Ph H
Ph O Ph LiAlD 4 Ph O O Ph O O D
H Ph H
H H H D D Ph H H Ph
H H Ph
Although recognizing the existence of the concerted cyclic mechanism, it has been
proposed that most preparative pyrolyses proceed as surface-catalyzed reactions. 336
Mixtures of alkenes are formed when more than one type of -hydrogen is
present. In acyclic compounds the product composition often approaches that expected
on a statistical basis from the number of each type of hydrogen. The E-alkene
usually predominates over the Z-alkene for a given isomeric pair. In cyclic struc-
tures, elimination is in the direction that the cyclic mechanism can operate most
favorably.
334 N. Kondo, H. Fueno, H. Fujimoto, M. Makino, H. Nakaoka, I. Aoki, and S. Uemura, J. Org. Chem.,
59, 5254 (1994).
335 D. Y. Curtin and D. B. Kellom, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 75, 6011 (1953).
336
D. H. Wertz and N. L. Allinger, J. Org. Chem., 42, 698 (1977).