Page 310 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 310
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 277
Chapter 5 E-business strategy 277
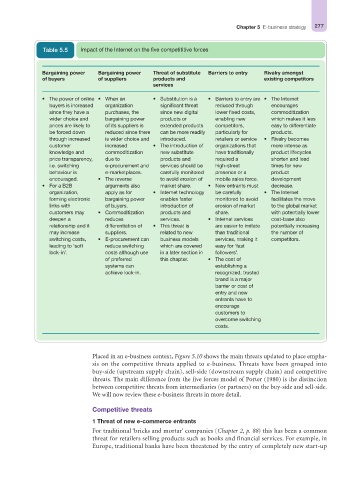
Table 5.5 Impact of the Internet on the five competititive forces
Bargaining power Bargaining power Threat of substitute Barriers to entry Rivalry amongst
of buyers of suppliers products and existing competitors
services
• The power of online • When an • Substitution is a • Barriers to entry are • The Internet
buyers is increased organization significant threat reduced through encourages
since they have a purchases, the since new digital lower fixed costs, commoditization
wider choice and bargaining power products or enabling new which makes it less
prices are likely to of its suppliers is extended products competitors, easy to differentiate
be forced down reduced since there can be more readily particularly for products.
through increased is wider choice and introduced. retailers or service • Rivalry becomes
customer increased • The introduction of organizations that more intense as
knowledge and commoditization new substitute have traditionally product lifecycles
price transparency, due to products and required a shorten and lead
i.e. switching e-procurement and services should be high-street times for new
behaviour is e-marketplaces. carefully monitored presence or a product
encouraged. • The reverse to avoid erosion of mobile sales force. development
• For a B2B arguments also market share. • New entrants must decrease.
organization, apply as for • Internet technology be carefully • The Internet
forming electronic bargaining power enables faster monitored to avoid facilitates the move
links with of buyers. introduction of erosion of market to the global market
customers may • Commoditization products and share. with potentially lower
deepen a reduces services. • Internet services cost-base also
relationship and it differentiation of • This threat is are easier to imitate potentially increasing
may increase suppliers. related to new than traditional the number of
switching costs, • E-procurement can business models services, making it competitors.
leading to ‘soft reduce switching which are covered easy for ‘fast
lock-in’. costs although use in a later section in followers’.
of preferred this chapter. • The cost of
systems can establishing a
achieve lock-in. recognized, trusted
brand is a major
barrier or cost of
entry and new
entrants have to
encourage
customers to
overcome switching
costs.
Placed in an e-business context, Figure 5.10 shows the main threats updated to place empha-
sis on the competitive threats applied to e-business. Threats have been grouped into
buy-side (upstream supply chain), sell-side (downstream supply chain) and competitive
threats. The main difference from the five forces model of Porter (1980) is the distinction
between competitive threats from intermediaries (or partners) on the buy-side and sell-side.
We will now review these e-business threats in more detail.
Competitive threats
1 Threat of new e-commerce entrants
For traditional ‘bricks and mortar’ companies (Chapter 2, p. 88) this has been a common
threat for retailers selling products such as books and financial services. For example, in
Europe, traditional banks have been threatened by the entry of completely new start-up