Page 437 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 437
428 Basic Control Systems Design
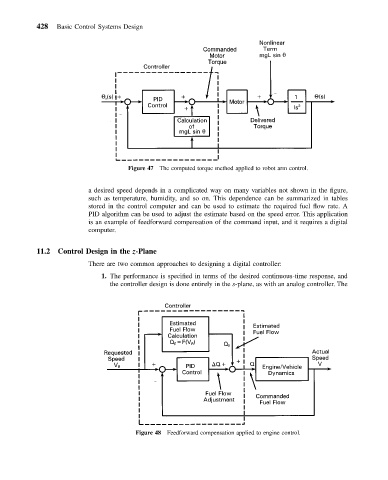
Figure 47 The computed torque method applied to robot arm control.
a desired speed depends in a complicated way on many variables not shown in the figure,
such as temperature, humidity, and so on. This dependence can be summarized in tables
stored in the control computer and can be used to estimate the required fuel flow rate. A
PID algorithm can be used to adjust the estimate based on the speed error. This application
is an example of feedforward compensation of the command input, and it requires a digital
computer.
11.2 Control Design in the z-Plane
There are two common approaches to designing a digital controller:
1. The performance is specified in terms of the desired continuous-time response, and
the controller design is done entirely in the s-plane, as with an analog controller. The
Figure 48 Feedforward compensation applied to engine control.