Page 768 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 768
2 The Pole Placement Design Method 759
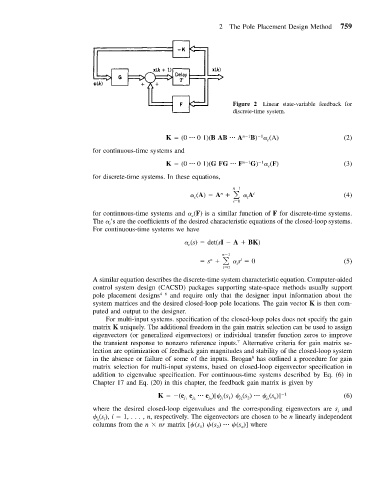
Figure 2 Linear state-variable feedback for
discrete-time system.
K (0 0 1)(BAB A n 1 B) (A) (2)
1
c
for continuous-time systems and
1
K (0 0 1)(GFG F n 1 G) (F) (3)
c
for discrete-time systems. In these equations,
(A) A A i (4)
n 1
n
c
i 0 i
for continuous-time systems and (F) is a similar function of F for discrete-time systems.
c
The ’s are the coefficients of the desired characteristic equations of the closed-loop systems.
i
For continuous-time systems we have
(s) det(sI A BK)
c
s s 0 (5)
n 1
i
n
i 0 i
A similar equation describes the discrete-time system characteristic equation. Computer-aided
control system design (CACSD) packages supporting state-space methods usually support
pole placement designs 4–6 and require only that the designer input information about the
system matrices and the desired closed-loop pole locations. The gain vector K is then com-
puted and output to the designer.
For multi-input systems. specification of the closed-loop poles does not specify the gain
matrix K uniquely. The additional freedom in the gain matrix selection can be used to assign
eigenvectors (or generalized eigenvectors) or individual transfer function zeros to improve
7
the transient response to nonzero reference inputs. Alternative criteria for gain matrix se-
lection are optimization of feedback gain magnitudes and stability of the closed-loop system
8
in the absence or failure of some of the inputs. Brogan has outlined a procedure for gain
matrix selection for multi-input systems, based on closed-loop eigenvector specification in
addition to eigenvalue specification. For continuous-time systems described by Eq. (6) in
Chapter 17 and Eq. (20) in this chapter, the feedback gain matrix is given by
K (ee e )[ (s ) (s ) (s )] 1 (6)
j 1 j 2 j n j 1 1 j 2 2 j n n
where the desired closed-loop eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors are s and
i
(s ), i 1,..., n, respectively. The eigenvectors are chosen to be n linearly independent
j i i
columns from the n nr matrix [ (s ) (s ) (s )] where
n
1
2