Page 445 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 445
Sensors in Flexible Manufacturing Systems
problem by hypothesizing massively parallel computers that can per- 399
form matching in linear time. Examples of these approaches include
graph matching, relaxation, and histogram analysis. The advantage
of these applications is that the decision is based on all the available
information at hand.
The basic principle of the local-feature-focus (LFF) method is to
find one feature of an image, referred to as the focus feature, and use it
to predict a few nearby features to look for. After finding some nearby
features, the program uses a graph-matching technique to identify
the largest cluster of image features matching a cluster of object fea-
tures. Since the list of possible object features has been reduced to
those near the focus feature, the graph is relatively small and can be
analyzed efficiently.
The key to the LFF method is an automatic feature-selection pro-
cedure that chooses the best focus features and the most useful sets of
nearby features. This automatic-programming capability makes pos-
sible quick and inexpensive application of the LFF method to new
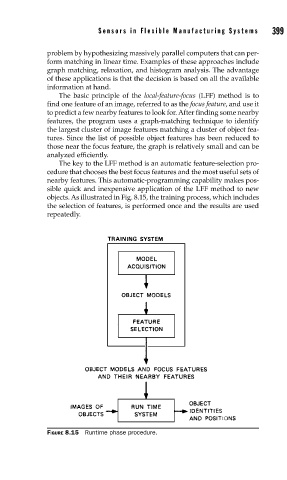
objects. As illustrated in Fig. 8.15, the training process, which includes
the selection of features, is performed once and the results are used
repeatedly.
FIGURE 8.15 Runtime phase procedure.