Page 1038 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1038
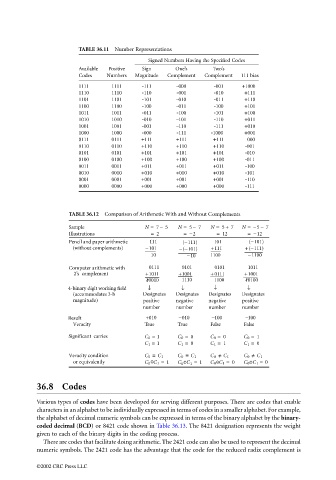
TABLE 36.11 Number Representations
Signed Numbers Having the Specified Codes
Available Positive Sign One’s Two’s
Codes Numbers Magnitude Complement Complement 111 bias
1111 1111 -111 -000 -001 +1000
1110 1110 -110 -001 -010 +111
1101 1101 -101 -010 -011 +110
1100 1100 -100 -011 -100 +101
1011 1011 -011 -100 -101 +100
1010 1010 -010 -101 -110 +011
1001 1001 -001 -110 -111 +010
1000 1000 -000 -111 -1000 +001
0111 0111 +111 +111 +111 000
0110 0110 +110 +110 +110 -001
0101 0101 +101 +101 +101 -010
0100 0100 +100 +100 +100 -011
0011 0011 +011 +011 +011 -100
0010 0010 +010 +010 +010 -101
0001 0001 +001 +001 +001 -110
0000 0000 +000 +000 +000 -111
TABLE 36.12 Comparison of Arithmetic With and Without Complements
Sample N = 7 − 5 N = 5 − 7 N = 5 + 7 N =−5 − 7
Illustrations = 2 =−2 = 12 =−12
Pencil and paper arithmetic 111 (−111) 101 (−101)
(without complements) −101 −(−101) +111 +(−111)
10 −10 1100 −1100
Computer arithmetic with 0111 0101 0101 1011
2’s complement +1011 +1001 + 0111 +1001
10010 1110 1100 10100
4-binary digit working field ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
(accommodates 3-b Designates Designates Designates Designates
magnitude) positive negative negative positive
number number number number
Result +010 −010 −100 −100
Veracity True True False False
Significant carries C 0 = 1 C 0 = 0 C 0 = 0 C 0 = 1
C 1 = 1 C 1 = 0 C 1 = 1 C 1 = 0
Veracity condition C 0 ≡ C 1 C 0 ≡ C 1 C 0 / ≡ C 1 C 0 / ≡ C 1
.
.
.
or equivalently C 0 C 1 = 1 C 0 C 1 = 1 C 0 C 1 = 0 C 0 C 1 = 0
.
36.8 Codes
Various types of codes have been developed for serving different purposes. There are codes that enable
characters in an alphabet to be individually expressed in terms of codes in a smaller alphabet. For example,
the alphabet of decimal numeric symbols can be expressed in terms of the binary alphabet by the binary-
coded decimal (BCD) or 8421 code shown in Table 36.13. The 8421 designation represents the weight
given to each of the binary digits in the coding process.
There are codes that facilitate doing arithmetic. The 2421 code can also be used to represent the decimal
numeric symbols. The 2421 code has the advantage that the code for the reduced radix complement is
©2002 CRC Press LLC