Page 344 - Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
P. 344
Core thermal hydraulics 313
Model Idealized conditions
DNS Sub
channel
level
LES
Physics Computational power
RANS Fuel assembly
level
Reduced resolution
RANS
Core
Low resolution level
CFD
CFD approaches Resolve Reactor conditions
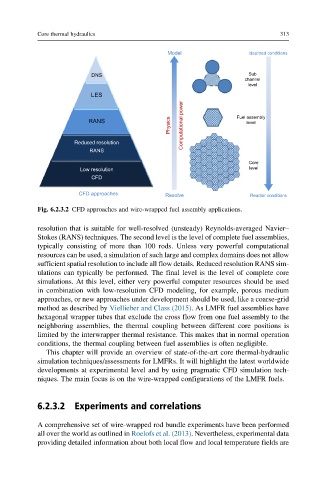
Fig. 6.2.3.2 CFD approaches and wire-wrapped fuel assembly applications.
resolution that is suitable for well-resolved (unsteady) Reynolds-averaged Navier–
Stokes (RANS) techniques. The second level is the level of complete fuel assemblies,
typically consisting of more than 100 rods. Unless very powerful computational
resources can be used, a simulation of such large and complex domains does not allow
sufficient spatial resolution to include all flow details. Reduced resolution RANS sim-
ulations can typically be performed. The final level is the level of complete core
simulations. At this level, either very powerful computer resources should be used
in combination with low-resolution CFD modeling, for example, porous medium
approaches, or new approaches under development should be used, like a coarse-grid
method as described by Viellieber and Class (2015). As LMFR fuel assemblies have
hexagonal wrapper tubes that exclude the cross flow from one fuel assembly to the
neighboring assemblies, the thermal coupling between different core positions is
limited by the interwrapper thermal resistance. This makes that in normal operation
conditions, the thermal coupling between fuel assemblies is often negligible.
This chapter will provide an overview of state-of-the-art core thermal-hydraulic
simulation techniques/assessments for LMFRs. It will highlight the latest worldwide
developments at experimental level and by using pragmatic CFD simulation tech-
niques. The main focus is on the wire-wrapped configurations of the LMFR fuels.
6.2.3.2 Experiments and correlations
A comprehensive set of wire-wrapped rod bundle experiments have been performed
all over the world as outlined in Roelofs et al. (2013). Nevertheless, experimental data
providing detailed information about both local flow and local temperature fields are