Page 113 - Cultural Theory
P. 113
Edwards-3516-Ch-05.qxd 5/9/2007 5:56 PM Page 102
••• John Scott •••
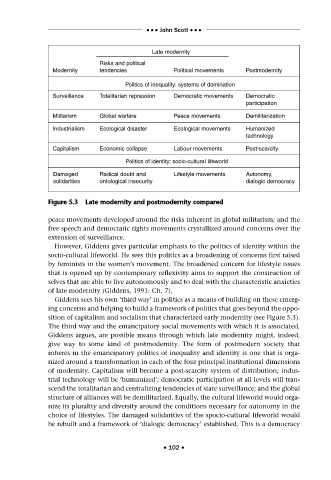
Late modernity
Risks and political
Modernity tendencies Political movements Postmodernity
Politics of inequality: systems of domination
Surveillance Totalitarian repression Democratic movements Democratic
participation
Militarism Global warfare Peace movements Demilitarization
Industrialism Ecological disaster Ecological movements Humanized
technology
Capitalism Economic collapse Labour movements Post-scarcity
Politics of identity: socio-cultural lifeworld
Damaged Radical doubt and Lifestyle movements Autonomy,
solidarities ontological insecurity dialogic democracy
p
n
i
r
d
e
t
n
d
a
y
o
m
c
y
e
d
r
p
a
t
m
o
t
o
s
n
i
r
d
e
e
r
5
i
F Figure 5.3 L Late modernity and postmodernity compared
u
g
e
o
m
a
3
.
t
peace movements developed around the risks inherent in global militarism; and the
free speech and democratic rights movements crystallized around concerns over the
extension of surveillance.
However, Giddens gives particular emphasis to the politics of identity within the
socio-cultural lifeworld. He sees this politics as a broadening of concerns first raised
by feminists in the women’s movement. The broadened concern for lifestyle issues
that is opened up by contemporary reflexivity aims to support the construction of
selves that are able to live autonomously and to deal with the characteristic anxieties
of late modernity (Giddens, 1991: Ch. 7).
Giddens sees his own ‘third way’ in politics as a means of building on these emerg-
ing concerns and helping to build a framework of politics that goes beyond the oppo-
sition of capitalism and socialism that characterized early modernity (see Figure 5.3).
The third way and the emancipatory social movements with which it is associated,
Giddens argues, are possible means through which late modernity might, indeed,
give way to some kind of postmodernity. The form of postmodern society that
inheres in the emancipatory politics of inequality and identity is one that is orga-
nized around a transformation in each of the four principal institutional dimensions
of modernity. Capitalism will become a post-scarcity system of distribution; indus-
trial technology will be ‘humanized’; democratic participation at all levels will tran-
scend the totalitarian and centralizing tendencies of state surveillance; and the global
structure of alliances will be demilitarized. Equally, the cultural lifeworld would orga-
nize its plurality and diversity around the conditions necessary for autonomy in the
choice of lifestyles. The damaged solidarities of the spocio-cultural lifeworld would
be rebuilt and a framework of ‘dialogic democracy’ established. This is a democracy
• 102 •