Page 58 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 58
42 2 Goal and Scope Definition
1 t municipal
waste
System A: incineration System B: landfill
Benefit: Benefit:
• 1 t municipal waste disposed • 1 t municipal waste disposed
Added value: System expansion:
• x MJ energy supply • x MJ energy supply
Indicator
environmental B + B′
impact A
(relative unit) B′
?
B
?
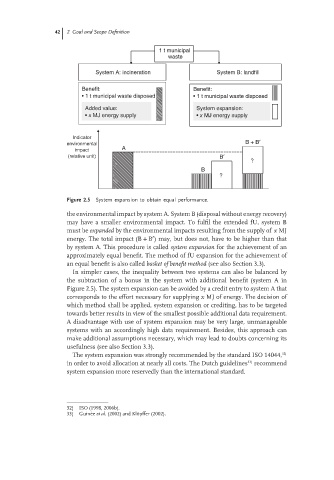
Figure 2.5 System expansion to obtain equal performance.
the environmental impact by system A. System B (disposal without energy recovery)
may have a smaller environmental impact. To fulfil the extended fU, system B
must be expanded by the environmental impacts resulting from the supply of x MJ
′
energy. The total impact (B + B ) may, but does not, have to be higher than that
by system A. This procedure is called system expansion for the achievement of an
approximately equal benefit. The method of fU expansion for the achievement of
an equal benefit is also called basket of benefit method (see also Section 3.3).
In simpler cases, the inequality between two systems can also be balanced by
the subtraction of a bonus in the system with additional benefit (system A in
Figure 2.5). The system expansion can be avoided by a credit entry to system A that
corresponds to the effort necessary for supplying x MJ of energy. The decision of
which method shall be applied, system expansion or crediting, has to be targeted
towards better results in view of the smallest possible additional data requirement.
A disadvantage with use of system expansion may be very large, unmanageable
systems with an accordingly high data requirement. Besides, this approach can
make additional assumptions necessary, which may lead to doubts concerning its
usefulness (see also Section 3.3).
The system expansion was strongly recommended by the standard ISO 14044, 32)
in order to avoid allocation at nearly all costs. The Dutch guidelines 33) recommend
system expansion more reservedly than the international standard.
32) ISO (1998, 2006b).
33) Guin´ ee et al. (2002) and Kl¨ opffer (2002).