Page 119 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 119
104 A. Bjørn et al.
Ecosphere
Technosphere
System boundaries
A/S
Reference flow
A/S
Legend
A/S
Process Product or Excluded Allocation/ Elementary
waste flow product or Substitution flow
waste flow
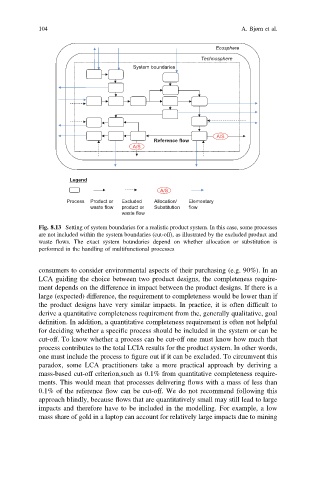
Fig. 8.13 Setting of system boundaries for a realistic product system. In this case, some processes
are not included within the system boundaries (cut-off), as illustrated by the excluded product and
waste flows. The exact system boundaries depend on whether allocation or substitution is
performed in the handling of multifunctional processes
consumers to consider environmental aspects of their purchasing (e.g. 90%). In an
LCA guiding the choice between two product designs, the completeness require-
ment depends on the difference in impact between the product designs. If there is a
large (expected) difference, the requirement to completeness would be lower than if
the product designs have very similar impacts. In practice, it is often difficult to
derive a quantitative completeness requirement from the, generally qualitative, goal
definition. In addition, a quantitative completeness requirement is often not helpful
for deciding whether a specific process should be included in the system or can be
cut-off. To know whether a process can be cut-off one must know how much that
process contributes to the total LCIA results for the product system. In other words,
one must include the process to figure out if it can be excluded. To circumvent this
paradox, some LCA practitioners take a more practical approach by deriving a
mass-based cut-off criterion,such as 0.1% from quantitative completeness require-
ments. This would mean that processes delivering flows with a mass of less than
0.1% of the reference flow can be cut-off. We do not recommend following this
approach blindly, because flows that are quantitatively small may still lead to large
impacts and therefore have to be included in the modelling. For example, a low
mass share of gold in a laptop can account for relatively large impacts due to mining