Page 232 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 232
218 R.K. Rosenbaum et al.
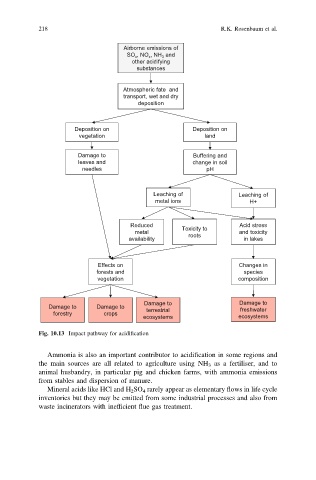
Airborne emissions of
SO x , NO x , NH 3 and
other acidifying
substances
Atmospheric fate and
transport, wet and dry
deposition
Deposition on Deposition on
vegetation land
Damage to Buffering and
leaves and change in soil
needles pH
Leaching of Leaching of
metal ions H+
Reduced Toxicity to Acid stress
metal roots and toxicity
availability in lakes
Effects on Changes in
forests and species
vegetation composition
Damage to Damage to
Damage to Damage to terrestrial freshwater
forestry crops
ecosystems ecosystems
Fig. 10.13 Impact pathway for acidification
Ammonia is also an important contributor to acidification in some regions and
the main sources are all related to agriculture using NH 3 as a fertiliser, and to
animal husbandry, in particular pig and chicken farms, with ammonia emissions
from stables and dispersion of manure.
Mineral acids like HCl and H 2 SO 4 rarely appear as elementary flows in life cycle
inventories but they may be emitted from some industrial processes and also from
waste incinerators with inefficient flue gas treatment.