Page 240 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 240
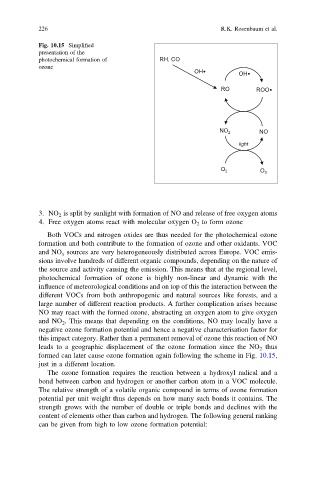
226 R.K. Rosenbaum et al.
Fig. 10.15 Simplified
presentation of the
photochemical formation of RH, CO
ozone
OH• OH•
RO ROO•
NO
NO 2
light
O 2
O 3
3. NO 2 is split by sunlight with formation of NO and release of free oxygen atoms
4. Free oxygen atoms react with molecular oxygen O 2 to form ozone
Both VOCs and nitrogen oxides are thus needed for the photochemical ozone
formation and both contribute to the formation of ozone and other oxidants. VOC
and NO x sources are very heterogeneously distributed across Europe. VOC emis-
sions involve hundreds of different organic compounds, depending on the nature of
the source and activity causing the emission. This means that at the regional level,
photochemical formation of ozone is highly non-linear and dynamic with the
influence of meteorological conditions and on top of this the interaction between the
different VOCs from both anthropogenic and natural sources like forests, and a
large number of different reaction products. A further complication arises because
NO may react with the formed ozone, abstracting an oxygen atom to give oxygen
and NO 2 . This means that depending on the conditions, NO may locally have a
negative ozone formation potential and hence a negative characterisation factor for
this impact category. Rather than a permanent removal of ozone this reaction of NO
leads to a geographic displacement of the ozone formation since the NO 2 thus
formed can later cause ozone formation again following the scheme in Fig. 10.15,
just in a different location.
The ozone formation requires the reaction between a hydroxyl radical and a
bond between carbon and hydrogen or another carbon atom in a VOC molecule.
The relative strength of a volatile organic compound in terms of ozone formation
potential per unit weight thus depends on how many such bonds it contains. The
strength grows with the number of double or triple bonds and declines with the
content of elements other than carbon and hydrogen. The following general ranking
can be given from high to low ozone formation potential: