Page 293 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 293
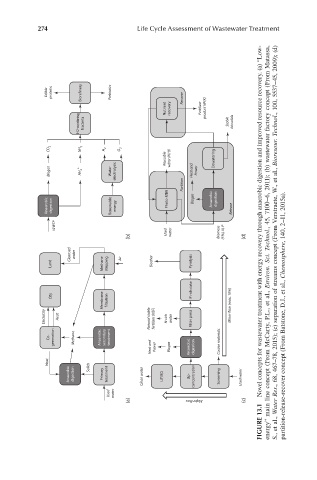
274 Life Cycle Assessment of Wastewater Treatment
Edible proteins Biore nery Prebiotics Recover
Nutrient recovery Fertilizer product NP(K)
H2-oxidizing bacteria Stable biosolids
CO 2 NH 3 H 2 O 2
Reusable wáter (N10) Dewatering
Biogas + NH 4 Water electrolysis Heat and Power
Partition
Anaerobic digestion Renewable energy Photo-MBR Biogas Anaerobic digestion Release
WWTP Novel concepts for wastewater treatment with energy recovery through anaerobic digestion and improved resource recovery. (a) “Low-
(b) Used water Biomass (5%), N, P (d) energy” main line concept (From McCarty, P.L., et al., Environ. Sci. Technol., 45, 7100–6, 2011); (b) wastewater factory concept (From Matassa, S., et al., Water Res., 68, 467–78, 2015); (c) separation of streams concept (From Verstraete, W., et al., Bioresour. Te
Cleansed water Air
Land Methane stripping Biochar Pyrolysis
P rich cake
Membrane ltration Minor ow (max. 10%)
City
Electricity Heat Natural stable fertilizer (NSF) N-rich water Filter press partition-release-recover concept (From Batstone, D.J., et al., Chemosphere, 140, 2–11, 2015a).
Co- generation Methane Anaerobic secondary treatment Coarse materials
Heat and Power Biogas Anaerobic digestion
Heat Solids
Anaerobic digestion Primary treatment Clean water UF/RO Up- concentration Screening Used water
Used water
(a) Major ow (c)
FIGURE 13.1