Page 302 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 302
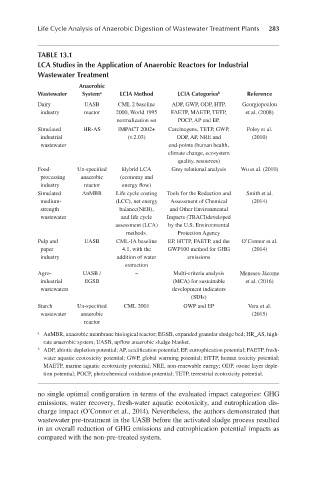
Life Cycle Analysis of Anaerobic Digestion of Wastewater Treatment Plants 283
TABLE 13.1
LCA Studies in the Application of Anaerobic Reactors for Industrial
Wastewater Treatment
Anaerobic
Wastewater System a LCIA Method LCIA Categories b Reference
Dairy UASB CML 2 baseline ADP, GWP, ODP, HTP, Georgiopoulou
industry reactor 2000, World 1995 FAETP, MAETP, TETP, et al. (2008)
normalization set POCP, AP and EP.
Simulated HR-AS IMPACT 2002+ Carcinogens, TETP, GWP, Foley et al.
industrial (v.2.03) ODP, AP, NRE and (2010)
wastewater end-points (human health,
climate change, ecosystem
quality, resources)
Food- Un-specified Hybrid LCA Grey relational analysis Wu et al. (2010)
processing anaerobic (economy and
industry reactor energy flow)
Simulated AnMBR Life cycle costing Tools for the Reduction and Smith et al.
medium- (LCC), net energy Assessment of Chemical (2014)
strength balance(NEB), and Other Environmental
wastewater and life cycle Impacts (TRACI)developed
assessment (LCA) by the U.S. Environmental
methods. Protection Agency
Pulp and UASB CML-IA baseline EP, HTTP, FAETP, and the O’Connor et al.
paper 4.1, with the GWP100 method for GHG (2014)
industry addition of water emissions
extraction
Agro- UASB / – Multi-criteria analysis Meneses-Jácome
industrial EGSB (MCA) for sustainable et al. (2016)
wastewaters development indicators
(SDIs)
Starch Un-specified CML 2001 GWP and EP Vera et al.
wastewater anaerobic (2015)
reactor
a AnMBR, anaerobic membrane biological reactor; EGSB, expanded granular sludge bed; HR_AS, high-
rate anaerobic system; UASB, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket.
b ADP, abiotic depletion potential; AP, acidification potential; EP, eutrophication potential; FAETP, fresh-
water aquatic ecotoxicity potential; GWP, global warming potential; HTTP, human toxicity potential;
MAETP, marine aquatic ecotoxicity potential; NRE, non-renewable energy; ODP, ozone layer deple-
tion potential; POCP, photochemical oxidation potential; TETP, terrestrial ecotoxicity potential.
no single optimal configuration in terms of the evaluated impact categories: GHG
emissions, water recovery, fresh-water aquatic ecotoxicity, and eutrophication dis-
charge impact (O’Connor et al., 2014). Nevertheless, the authors demonstrated that
wastewater pre-treatment in the UASB before the activated sludge process resulted
in an overall reduction of GHG emissions and eutrophication potential impacts as
compared with the non-pre-treated system.