Page 43 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 43
26 Practical Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation
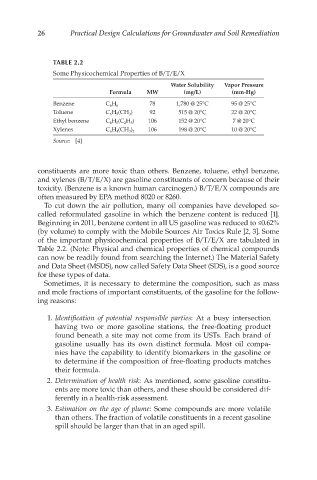
TABLE 2.2
Some Physicochemical Properties of B/T/E/X
Water Solubility Vapor Pressure
Formula MW (mg/L) (mm-Hg)
Benzene C 6 H 6 78 1,780 @ 25°C 95 @ 25°C
Toluene C 6 H 5 (CH 3 ) 92 515 @ 20°C 22 @ 20°C
Ethyl benzene C 6 H 5 (C 2 H 5 ) 106 152 @ 20°C 7 @ 20°C
Xylenes C 6 H 4 (CH 3 ) 2 106 198 @ 20°C 10 @ 20°C
Source: [4]
constituents are more toxic than others. Benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene,
and xylenes (B/T/E/X) are gasoline constituents of concern because of their
toxicity. (Benzene is a known human carcinogen.) B/T/E/X compounds are
often measured by EPA method 8020 or 8260.
To cut down the air pollution, many oil companies have developed so-
called reformulated gasoline in which the benzene content is reduced [1].
Beginning in 2011, benzene content in all US gasoline was reduced to ≤0.62%
(by volume) to comply with the Mobile Sources Air Toxics Rule [2, 3]. Some
of the important physicochemical properties of B/T/E/X are tabulated in
Table 2.2. (Note: Physical and chemical properties of chemical compounds
can now be readily found from searching the Internet.) The Material Safety
and Data Sheet (MSDS), now called Safety Data Sheet (SDS), is a good source
for these types of data.
Sometimes, it is necessary to determine the composition, such as mass
and mole fractions of important constituents, of the gasoline for the follow-
ing reasons:
1. Identification of potential responsible parties: At a busy intersection
having two or more gasoline stations, the free-floating product
found beneath a site may not come from its USTs. Each brand of
gasoline usually has its own distinct formula. Most oil compa-
nies have the capability to identify biomarkers in the gasoline or
to determine if the composition of free-floating products matches
their formula.
2. Determination of health risk: As mentioned, some gasoline constitu-
ents are more toxic than others, and these should be considered dif-
ferently in a health-risk assessment.
3. Estimation on the age of plume: Some compounds are more volatile
than others. The fraction of volatile constituents in a recent gasoline
spill should be larger than that in an aged spill.