Page 64 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 64
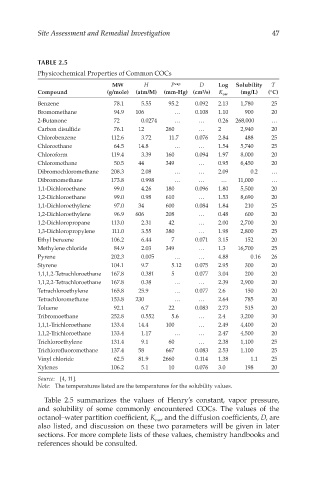
Site Assessment and Remedial Investigation 47
TABLE 2.5
Physicochemical Properties of Common COCs
MW H P vap D Log Solubility T
2
Compound (g/mole) (atm/M) (mm-Hg) (cm /s) K ow (mg/L) (°C)
Benzene 78.1 5.55 95.2 0.092 2.13 1,780 25
Bromomethane 94.9 106 … 0.108 1.10 900 20
2-Butanone 72 0.0274 … … 0.26 268,000 …
Carbon disulfide 76.1 12 260 … 2 2,940 20
Chlorobenzene 112.6 3.72 11.7 0.076 2.84 488 25
Chloroethane 64.5 14.8 … … 1.54 5,740 25
Chloroform 119.4 3.39 160 0.094 1.97 8,000 20
Chloromethane 50.5 44 349 … 0.95 6,450 20
Dibromochloromethane 208.3 2.08 … … 2.09 0.2 …
Dibromomethane 173.8 0.998 … … … 11,000 …
1,1-Dichloroethane 99.0 4.26 180 0.096 1.80 5,500 20
1,2-Dichloroethane 99.0 0.98 610 … 1.53 8,690 20
1,1-Dichloroethylene 97.0 34 600 0.084 1.84 210 25
1,2-Dichloroethylene 96.9 606 208 … 0.48 600 20
1,2-Dichloropropane 113.0 2.31 42 … 2.00 2,700 20
1,3-Dichloropropylene 111.0 3.55 380 … 1.98 2,800 25
Ethyl benzene 106.2 6.44 7 0.071 3.15 152 20
Methylene chloride 84.9 2.03 349 … 1.3 16,700 25
Pyrene 202.3 0.005 … … 4.88 0.16 26
Styrene 104.1 9.7 5.12 0.075 2.95 300 20
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane 167.8 0.381 5 0.077 3.04 200 20
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane 167.8 0.38 … … 2.39 2,900 20
Tetrachloroethylene 165.8 25.9 … 0.077 2.6 150 20
Tetrachloromethane 153.8 230 … … 2.64 785 20
Toluene 92.1 6.7 22 0.083 2.73 515 20
Tribromoethane 252.8 0.552 5.6 … 2.4 3,200 30
1,1,1-Trichloroethane 133.4 14.4 100 … 2.49 4,400 20
1,1,2-Trichloroethane 133.4 1.17 … … 2.47 4,500 20
Trichloroethylene 131.4 9.1 60 … 2.38 1,100 25
Trichlorofluoromethane 137.4 58 667 0.083 2.53 1,100 25
Vinyl chloride 62.5 81.9 2660 0.114 1.38 1.1 25
Xylenes 106.2 5.1 10 0.076 3.0 198 20
Source: [4, 11].
Note: The temperatures listed are the temperatures for the solubility values.
Table 2.5 summarizes the values of Henry’s constant, vapor pressure,
and solubility of some commonly encountered COCs. The values of the
octanol–water partition coefficient, K , and the diffusion coefficients, D, are
ow
also listed, and discussion on these two parameters will be given in later
sections. For more complete lists of these values, chemistry handbooks and
references should be consulted.