Page 114 - The ISA Handbook in Contemporary Sociology
P. 114
9781412934633-Chap-06 1/10/09 8:46 AM Page 85
RELATING AUTHORITY AND SOLIDARITY 85
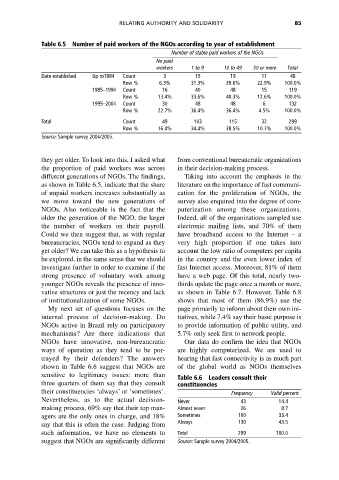
Table 6.5 Number of paid workers of the NGOs according to year of establishment
Number of stable paid workers of the NGOs
No paid
workers 1 to 9 10 to 49 50 or more Total
Date established Up to1984 Count 3 15 19 11 48
Row % 6.3% 31.3% 39.6% 22.9% 100.0%
1985–1994 Count 16 40 48 15 119
Row % 13.4% 33.6% 40.3% 12.6% 100.0%
1995–2004 Count 30 48 48 6 132
Row % 22.7% 36.4% 36.4% 4.5% 100.0%
Total Count 49 103 115 32 299
Row % 16.4% 34.4% 38.5% 10.7% 100.0%
Source: Sample survey 2004/2005.
they get older. To look into this, I asked what from conventional bureaucratic organizations
the proportion of paid workers was across in their decision-making process.
different generations of NGOs. The findings, Taking into account the emphasis in the
as shown in Table 6.5, indicate that the share literature on the importance of fast communi-
of unpaid workers increases substantially as cation for the proliferation of NGOs, the
we move toward the new generations of survey also enquired into the degree of com-
NGOs. Also noticeable is the fact that the puterization among these organizations.
older the generation of the NGO, the larger Indeed, all of the organizations sampled use
the number of workers on their payroll. electronic mailing lists, and 70% of them
Could we then suggest that, as with regular have broadband access to the Internet – a
bureaucracies, NGOs tend to expand as they very high proportion if one takes into
get older? We can take this as a hypothesis to account the low ratio of computers per capita
be explored, in the same sense that we should in the country and the even lower index of
investigate further in order to examine if the fast Internet access. Moreover, 81% of them
strong presence of voluntary work among have a web page. Of this total, nearly two-
younger NGOs reveals the presence of inno- thirds update the page once a month or more,
vative structures or just the recency and lack as shown in Table 6.7. However, Table 6.8
of institutionalization of some NGOs. shows that most of them (86.9%) use the
My next set of questions focuses on the page primarily to inform about their own ini-
internal process of decision-making. Do tiatives, while 7.4% say their basic purpose is
NGOs active in Brazil rely on participatory to provide information of public utility, and
mechanisms? Are there indications that 5.7% only seek first to network people.
NGOs have innovative, non-bureaucratic Our data do confirm the idea that NGOs
ways of operation as they tend to be por- are highly computerized. We are used to
trayed by their defenders? The answers hearing that fast connectivity is as much part
shown in Table 6.6 suggest that NGOs are of the global world as NGOs themselves
sensitive to legitimacy issues: more than
Table 6.6 Leaders consult their
three quarters of them say that they consult constituencies
their constituencies ‘always’ or ‘sometimes’. Frequency Valid percent
Nevertheless, as to the actual decision- Never 43 14.4
making process, 69% say that their top man- Almost never 26 8.7
agers are the only ones in charge, and 18% Sometimes 100 33.4
say that this is often the case. Judging from Always 130 43.5
such information, we have no elements to Total 299 100.0
suggest that NGOs are significantly different Source: Sample survey 2004/2005.