Page 185 - A Practical Companion to Reservoir Stimulation
P. 185
PRACTICAL COMPANION TO RESERVOIR STIMULATION
P-3.3: Friction Pressure Drop through 2%-in. tubing, the friction pressure drop is also 320
The pumping of highly non-Newtonian viscoelastic fluids psi/lOOO ft. Large differences will be observed at low flow
results in significant pressure drops through the treating rates in small-diameter tubings.
tubulars. These pressure drops cannot be calculated readily Figures P-3 1 through P-33 contain the friction pressure
through the classic Reynolds numbedfriction pressure drop drop for 40-lb, 50-lb and 60-lb zirconates, respectively.
methods. Thus, experimental data are necessary, especially in Figures P-34 through P-37 contain friction pressure drops
turbulent flow. for foams of various qualities in 2%-, 2%-, 4%- and 5%-in.
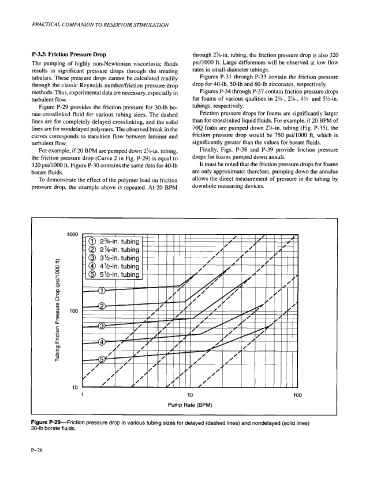
Figure P-29 provides the friction pressure for 30-lb bo- tubings, respectively.
rate-crosslinked fluid for various tubing sizes. The dashed Friction pressure drops for foams are significantly larger
lines are for completely delayed crosslinking, and the solid than for crosslinked liquid fluids. For example, if 20 BPM of
lines are for nondelayed polymers. The observed break in the 704 foam are pumped down 2x411. tubing (Fig. P-35), the
curves corresponds to transition flow between laminar and friction pressure drop would be 750 psi/lOOO ft, which is
turbulent flow. significantly greater than the values for borate fluids.
For example, if 20 BPM are pumped down 2%-in. tubing, Finally, Figs. P-38 and P-39 provide friction pressure
the friction pressure drop (Curve 2 in Fig. P-29) is equal to drops for foams pumped down annuli.
320 psi/lOOO ft. Figure P-30 contains the same data for 40-lb It must be noted that the friction pressure drops for foams
borate fluids. are only approximate; therefore, pumping down the annulus
To demonstrate the effect of the polymer load on friction allows the direct measurement of pressure in the tubing by
pressure drop, the example above is repeated. At 20 BPM downhole measuring devices.
1000
100
10
1 10 100
Pump Rate (BPM)
Figure P-29-Friction pressure drop in various tubing sizes for delayed (dashed lines) and nondelayed (solid lines)
30-lb borate fluids.
P-26