Page 15 - A Practical Introduction to Optical Mineralogy
P. 15
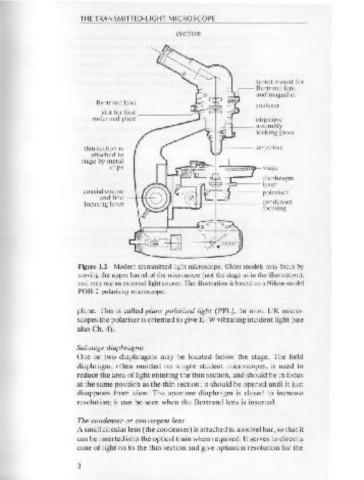
THE TRANSMITTED-LIGHT MICROSCOPE
eyepiece
head securing
turret mount for
Bertrand lens
and magnifier
Bertrand lens -------~~~~;,_~b.-- analyser
slot for first _______ _,-
order red plate objective
+ -- assembly
locking piece
thin section is
attached to
stage by metal - lt------"----------1---,
cl ips "":~iD'i'i'i'1'i!!iip- stage
diaphragm
-:.:;)---- lever
coaxial coarse 1..-t=T"'--o~---- polariscr
and fine
focusing lever 1 -~~!1--t _______ condcnser
1- focusing
Figure 1.2 Modern transmitted light microscope. Older models may focus by
moving the upper barrel of the microscope (not the stage as in the illustration),
and may use an external light source. The illustration is based on a Nikon model
on/off switch POH-2 polarising microscope.
(intensity
control)
plane. This is called plane polarised light (PPL). In most UK micro-
scopes the polariser is oriented to give E-W vibrating incident light (see
Model MP 3502M also Ch. 4).
*Analyser
The analyser is located on the Substage diaphragms
left-hand side of the head mounting One or two diaphragms may be located below the stage. The field
block on all MP3.500 microscope
models diaphragm, often omitted on simple student microscopes, is used to
reduce the area of light entering the thin section, and should be in focus
at the same position as the thin section ; it should be opened until it just
disappears from view. The aperture diaphragm is closed to increase
resolution; it can be seen when the Bertrand lens is inserted.
Figure 1.1 The Swift Student polarising microscope (photo courtesy of Swift
Ltd). The condenser or convergent lens
A small circular lens (the condenser) is attached to a swivel bar, so that it
can be inserted·into the optical train when required. It serves to direct a
cone of light on to the thin section and give optimum resolution for the
2 3