Page 59 - Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection by S.E. Hughes, Clifford Matthews
P. 59
A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
Heat treatment of steels
Metallic materials consist of a microstructure of small
crystals called grains. The grain size and composition help
determine the overall mechanical behaviour of the metal.
Heat treatment provides an efficient way to manipulate the
properties of the metal by controlling the formation of
structures, changing the metal properties or controlling the
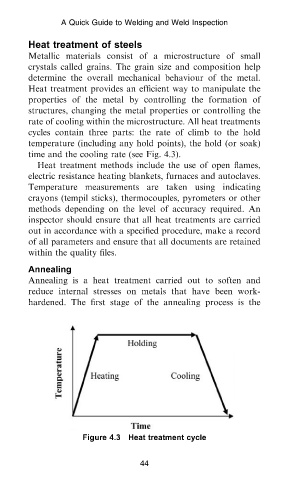
rate of cooling within the microstructure. All heat treatments
cycles contain three parts: the rate of climb to the hold
temperature (including any hold points), the hold (or soak)
time and the cooling rate (see Fig. 4.3).
Heat treatment methods include the use of open flames,
electric resistance heating blankets, furnaces and autoclaves.
Temperature measurements are taken using indicating
crayons (tempil sticks), thermocouples, pyrometers or other
methods depending on the level of accuracy required. An
inspector should ensure that all heat treatments are carried
out in accordance with a specified procedure, make a record
of all parameters and ensure that all documents are retained
within the quality files.
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment carried out to soften and
reduce internal stresses on metals that have been work-
hardened. The first stage of the annealing process is the
Figure 4.3 Heat treatment cycle
44
Woodhead Publishing Ltd – A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
Data Standards Ltd, Frome, Somerset – 17/9/200904QG Welding chap4.3d Page 44 of 48