Page 77 - Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection by S.E. Hughes, Clifford Matthews
P. 77
A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
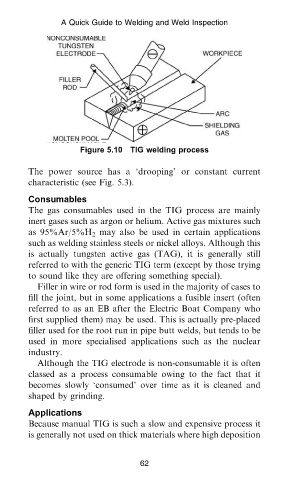
Figure 5.10 TIG welding process
The power source has a ‘drooping’ or constant current
characteristic (see Fig. 5.3).
Consumables
The gas consumables used in the TIG process are mainly
inert gases such as argon or helium. Active gas mixtures such
as 95%Ar/5%H 2 may also be used in certain applications
such as welding stainless steels or nickel alloys. Although this
is actually tungsten active gas (TAG), it is generally still
referred to with the generic TIG term (except by those trying
to sound like they are offering something special).
Filler in wire or rod form is used in the majority of cases to
fill the joint, but in some applications a fusible insert (often
referred to as an EB after the Electric Boat Company who
first supplied them) may be used. This is actually pre-placed
filler used for the root run in pipe butt welds, but tends to be
used in more specialised applications such as the nuclear
industry.
Although the TIG electrode is non-consumable it is often
classed as a process consumable owing to the fact that it
becomes slowly ‘consumed’ over time as it is cleaned and
shaped by grinding.
Applications
Because manual TIG is such a slow and expensive process it
is generally not used on thick materials where high deposition
62
Woodhead Publishing Ltd – A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
Data Standards Ltd, Frome, Somerset – 17/9/200905QG Welding chap5.3d Page 62 of 66