Page 26 - A Working Method Approach For Introductory Physical Chemistry Calculations
P. 26
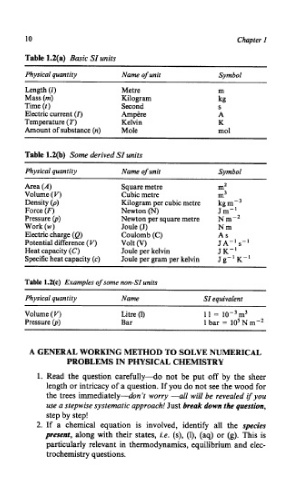
10 Chapter I
Table 1.2(a) Basic SI units
Physical quantity Name of unit Symbol
Length (1) Metre m
Mass (m) Kilogram kg
Time (t ) Second S
Electric current (I) Ampere A
Temperature (T) Kelvin K
Amount of substance (n) Mole mol
Table 1.2(b) Some derived SI units
Physical quantity Name of unit Symbol
Area (A) Square metre m2
Volume (V) Cubic metre m3
Density (p) Kilogram per cubic metre kg m-’
Force (F) Newton (N) Jm-’
Pressure (p) Newton per square metre N m-’
Work (w) Joule (J) Nm
Electric charge (Q) Coulomb (C) As
Potential difference (V) Volt (v) JA-: s-I
Heat capacity (C) Joule per kelvin J K-
Specific heat capacity (c) Joule per gram per kelvin J g-’ K-’
Table 1.2(c) Examples of some nun-SI units
Physical quantity Name SI equivalent
~~
Volume (V) Litre (1) 1 I = 10-3m3
Pressure (p) Bar 1 bar = 10’ N m-’
A GENERAL WORKING METHOD TO SOLVE NUMERICAL
PROBLEMS IN PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Read the question carefully-do not be put off by the sheer
length or intricacy of a question. If you do not see the wood for
the trees immediately-don’t worry -all will be revealed if you
use a stepwise systematic approach! Just break down the question,
step by step!
If a chemical equation is involved, identify all the species
present, along with their states, i.e. (s), (l), (as) or (8). This is
particularly relevant in thermodynamics, equilibrium and elec-
trochemistry questions.