Page 296 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 296
Non-integral mathematics 285
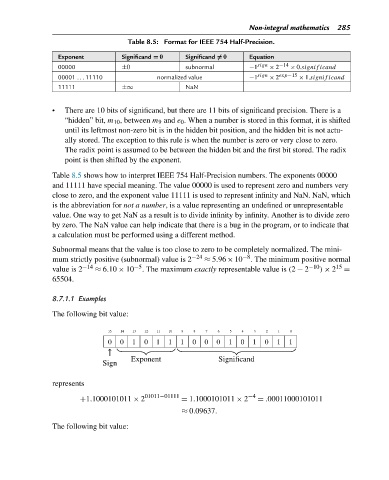
Table 8.5: Format for IEEE 754 Half-Precision.
Exponent Significand = 0 Significand = 0 Equation
00000 ±0 subnormal −1 sign × 2 −14 × 0.signif icand
00001 . . . 11110 normalized value −1 sign × 2 exp−15 × 1.signif icand
11111 ±∞ NaN
• There are 10 bits of significand, but there are 11 bits of significand precision. There is a
“hidden” bit, m 10 , between m 9 and e 0 . When a number is stored in this format, it is shifted
until its leftmost non-zero bit is in the hidden bit position, and the hidden bit is not actu-
ally stored. The exception to this rule is when the number is zero or very close to zero.
The radix point is assumed to be between the hidden bit and the first bit stored. The radix
point is then shifted by the exponent.
Table 8.5 shows how to interpret IEEE 754 Half-Precision numbers. The exponents 00000
and 11111 have special meaning. The value 00000 is used to represent zero and numbers very
close to zero, and the exponent value 11111 is used to represent infinity and NaN. NaN, which
is the abbreviation for not a number, is a value representing an undefined or unrepresentable
value. One way to get NaN as a result is to divide infinity by infinity. Another is to divide zero
by zero. The NaN value can help indicate that there is a bug in the program, or to indicate that
a calculation must be performed using a different method.
Subnormal means that the value is too close to zero to be completely normalized. The mini-
mum strictly positive (subnormal) value is 2 −24 ≈ 5.96×10 −8 . The minimum positive normal
value is 2 −14 ≈ 6.10 × 10 −5 . The maximum exactly representable value is (2 − 2 −10 ) × 2 15 =
65504.
8.7.1.1 Examples
The following bit value:
represents
+1.1000101011 × 2 01011−01111 = 1.1000101011 × 2 −4 = .00011000101011
≈ 0.09637.
The following bit value: