Page 97 - Adaptive Identification and Control of Uncertain Systems with Nonsmooth Dynamics
P. 97
RISE Based Asymptotic PPC of Servo Systems With Continuously Differentiable Friction Model 89
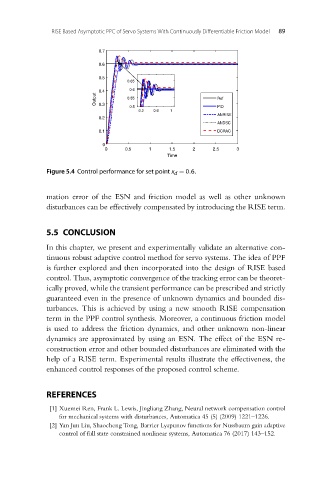
Figure 5.4 Control performance for set point x = 0.6.
d
mation error of the ESN and friction model as well as other unknown
disturbances can be effectively compensated by introducing the RISE term.
5.5 CONCLUSION
In this chapter, we present and experimentally validate an alternative con-
tinuous robust adaptive control method for servo systems. The idea of PPF
is further explored and then incorporated into the design of RISE based
control. Thus, asymptotic convergence of the tracking error can be theoret-
ically proved, while the transient performance can be prescribed and strictly
guaranteed even in the presence of unknown dynamics and bounded dis-
turbances. This is achieved by using a new smooth RISE compensation
term in the PPF control synthesis. Moreover, a continuous friction model
is used to address the friction dynamics, and other unknown non-linear
dynamics are approximated by using an ESN. The effect of the ESN re-
construction error and other bounded disturbances are eliminated with the
help of a RISE term. Experimental results illustrate the effectiveness, the
enhanced control responses of the proposed control scheme.
REFERENCES
[1] Xuemei Ren, Frank L. Lewis, Jingliang Zhang, Neural network compensation control
for mechanical systems with disturbances, Automatica 45 (5) (2009) 1221–1226.
[2] Yan Jun Liu, Shaocheng Tong, Barrier Lyapunov functions for Nussbaum gain adaptive
control of full state constrained nonlinear systems, Automatica 76 (2017) 143–152.