Page 224 - Adsorbents - fundamentals and applications
P. 224
NATURE OF π-COMPLEXATION BONDING 209
+
2+
+
+
benzene/halides of Cu ,Pd ,Ag ,Au ,and Pt 4+ (Takahashi et al., 2000);
thiophene/CuCl and AgCl (Yang et al., 2001); and thiophene/Ag-zeolite and Cu-
zeolite (Takahashi et al., 2002). The results of adsorption of C 2 H 4 on Ag halides
and Ag-zeolite will be discussed first.
8.3.1. Understanding π-Complexation Bond through Molecular Orbital
Theory
The geometries of C 2 H 4 , AgX (where X = halide), and Ag-zeolite are opti-
mized first, using STO-3G and then at the 3-21G levels. The cluster model
(Kassab et al., 1993; Hill and Sauer, 1995) is used to represent the chemistry of
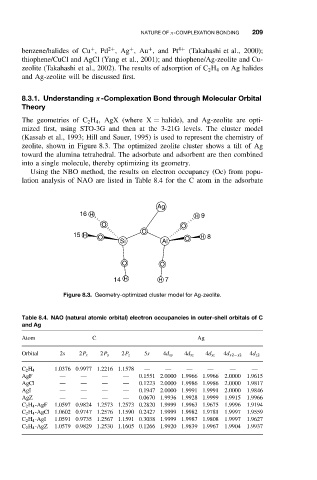
zeolite, shown in Figure 8.3. The optimized zeolite cluster shows a tilt of Ag
toward the alumina tetrahedral. The adsorbate and adsorbent are then combined
into a single molecule, thereby optimizing its geometry.
Using the NBO method, the results on electron occupancy (Oc) from popu-
lation analysis of NAO are listed in Table 8.4 for the C atom in the adsorbate
Ag
16 H H 9
O O
O
15 H
O O H 8
Si Al
O O
14 H H 7
Figure 8.3. Geometry-optimized cluster model for Ag-zeolite.
Table 8.4. NAO (natural atomic orbital) electron occupancies in outer-shell orbitals of C
and Ag
Atom C Ag
Orbital 2s 2P x 2P y 2P z 5s 4d xy 4d xz 4d yz 4d x2−y2 4d z2
C 2 H 4 1.0376 0.9977 1.2216 1.1578 — — — — — —
AgF — — — — 0.1551 2.0000 1.9966 1.9966 2.0000 1.9615
AgCl — — — — 0.1223 2.0000 1.9986 1.9986 2.0000 1.9817
AgI — — — — 0.1947 2.0000 1.9991 1.9991 2.0000 1.9846
AgZ — — — — 0.0670 1.9936 1.9928 1.9999 1.9915 1.9966
C 2 H 4 -AgF 1.0597 0.9824 1.2573 1.2573 0.2820 1.9999 1.9963 1.9675 1.9996 1.9194
C 2 H 4 -AgCl 1.0602 0.9747 1.2576 1.1590 0.2427 1.9999 1.9982 1.9781 1.9997 1.9559
C 2 H 4 -AgI 1.0591 0.9735 1.2567 1.1591 0.3038 1.9999 1.9987 1.9808 1.9997 1.9627
C 2 H 4 -AgZ 1.0579 0.9829 1.2530 1.1605 0.1266 1.9920 1.9839 1.9967 1.9904 1.9937