Page 207 - Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids
P. 207
F
CHflER 7. ASSESSMENT OF MESOPOROSlTY
contact of the particles. The initial interparticle condensation is reversible, but as the
menisci meet the narrow openings between the particles (i.e, the 'win-
dows' or 'throats') are spontaneously filled. The third stage involves the filling of the
larger voids (or cavities) within the packed particles.
The initial process of monolayer-multilayer adsorption on the available surface of
fie packed spherical particles is complicated by two opposing effects. First, there is
Jways a significant reduction in adsorption due to the loss of surface area between
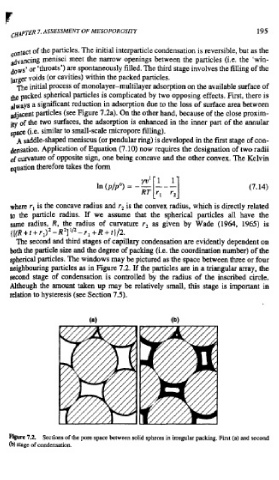
djacent particles (see Figure 7.24. On the other hand, because of the close proxim-
ity of the two surfaces, the adsorption is enhanced in the inner part of the annular
spilce (i.e. similar to small-scale micropore filling).
A saddle-shaped meniscus (or pendular ring) is developed in the first stage of con-
densation. Application of Equation (7.10) now requires the designation of two radii
of curvature of opposite sign, one being concave and the other convex. The Kelvin
therefore takes the form
where r, is the concave radius and r, is the convex radius, which is directly related
to the particle radius. If we assume that the spherical particles all have the
same radius, R, the radius of curvature r, as given by Wade (1964, 1965) is
+R+
t)/2.
{[(~+t+r,)~-~~]'~~-r~
The second and third stages of capillary condensation are evidently dependent on
both the particle size and the degree of packing (i.e. the coordination number) of the
spherical particles. The windows may be pictured as the space between three or four
neighbouring particles as in Figure 7.2. If the particles are in a triangular array, the
second stage of condensation is controlled by the radius of the inscribed circle.
Although the amount taken up may be relatively small, this stage is important in
relation to hysteresis (see Section 7.5).
Hgure 7.2. Sections of the pore space between solid spheres in irregular packing. First (a) and second
(b) Stage of condensation.