Page 164 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 164
Chapter 8. Novel gas turbine cycles 133
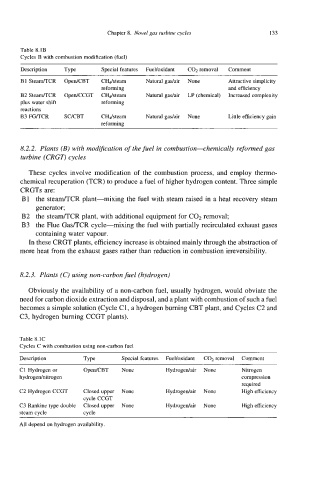
Table 8.1B
Cycles B with combustion modification (fuel)
Description Type Special features FueVoxidant C@ removal Comment
BI Steam/TCR OpedCBT CH.,/steam Naturalgadair None Attractive simplicity
reforming and efficiency
B2 StedCR OpedCCGT CH.,/steam Natural gadair LP (chemical) Increased complexity
plus water shift reforming
reactions
B3FGRCR SUCBT CH.,/steam Natural gadair None Little efficiency gain
reforming
8.2.2. Plants (B) with modifcation of the fuel in combustion-chemically reformed gas
turbine (CRGT) cycles
These cycles involve modification of the combustion process, and employ thermo-
chemical recuperation (TCR) to produce a fuel of higher hydrogen content. Three simple
CRGTs are:
B1 the steam/TCR plant-mixing the fuel with steam raised in a heat recovery steam
generator;
B2 the steam/TCR plant, with additional equipment for C02 removal;
B3 the Flue GasmCR cycle-mixing the fuel with partially recirculated exhaust gases
containing water vapour.
In these CRGT plants, efficiency increase is obtained mainly through the abstraction of
more heat from the exhaust gases rather than reduction in combustion irreversibility.
8.2.3. Plants (C) using non-carbon fuel (hydrogen)
Obviously the availability of a non-carbon fuel, usually hydrogen, would obviate the
need for carbon dioxide extraction and disposal, and a plant with combustion of such a fuel
becomes a simple solution (Cycle C1, a hydrogen burning CBT plant, and Cycles C2 and
C3, hydrogen burning CCGT plants).
Table 8. IC
Cycles C with combustion using non-carbon fuel
Description Type Special features FueVoxidant CO2 removal Comment
C1 Hydrogen or OpedCBT None Hydrogedair None Nitrogen
hydrogednitrogen compression
required
C2 Hydrogen CCGT Closed upper None Hydrogedair None High efficiency
cycle CCGT
C3 Rankine type double Closed upper None Hydrogedair None High efficiency
steam cvcle cvcle
All depend on hydrogen availability.