Page 198 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 198
184 CHAPTER 9 THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF IDEAL GASES
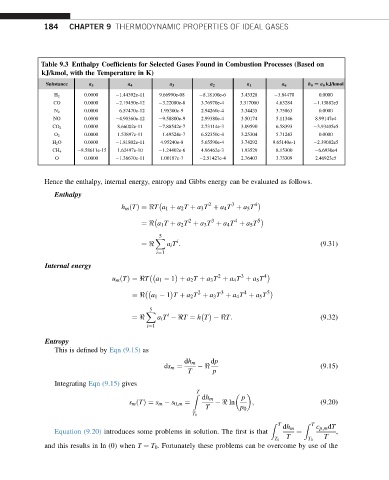
Table 9.3 Enthalpy Coefficients for Selected Gases Found in Combustion Processes (Based on
kJ/kmol, with the Temperature in K)
Substance a 5 a 4 a 3 a 2 a 1 a 6 h 0 [ a 0 kJ/kmol
H 2 0.0000 1.44392e-11 9.66990e-08 8.18100e-6 3.43328 3.84470 0.0000
CO 0.0000 2.19450e-12 3.22080e-8 3.76970e-4 3.317000 4.63284 1.13882e5
N 2 0.0000 6.57470e-12 1.95300e-9 2.94260e-4 3.34435 3.75863 0.0000
NO 0.0000 4.90360e-12 9.58800e-9 2.99380e-4 3.50174 5.11346 8.99147e4
0.0000 8.66002e-11 7.88542e-7 2.73114e-3 3.09590 6.58393 3.93405e5
CO 2
0.0000 1.53897e-11 1.49524e-7 6.52350e-4 3.25304 5.71243 0.0000
O 2
H 2 O 0.0000 1.81802e-11 4.95240e-8 5.65590e-4 3.74292 9.65140e-1 2.39082e5
8.58611e-15 1.62497e-10 1.24402e-6 4.96462e-3 1.93529 8.15300 6.6930e4
CH 4
O 0.0000 1.38670e-11 1.00187e-7 2.51427e-4 2.76403 3.73309 2.46923e5
Hence the enthalpy, internal energy, entropy and Gibbs energy can be evaluated as follows.
Enthalpy
2 3 4
h m ðTÞ¼<T a 1 þ a 2 T þ a 3 T þ a 4 T þ a 5 T
2 3 4 5
¼< a 1 T þ a 2 T þ a 3 T þ a 4 T þ a 5 T
5
X i
¼< a i T : (9.31)
i¼1
Internal energy
2 3 4
u m ðTÞ¼<T a 1 1 þ a 2 T þ a 3 T þ a 4 T þ a 5 T
2 3 4 5
¼< a 1 1 T þ a 2 T þ a 3 T þ a 4 T þ a 5 T
5
X i
¼< a i T <T ¼ h T <T: (9.32)
i¼1
Entropy
This is defined by Eqn (9.15) as
dp
dh m
ds m ¼ < (9.15)
T p
Integrating Eqn (9.15) gives
T
Z
dh m p
s m ðTÞ¼ s m s 0;m ¼ < ln ; (9.20)
T p 0
T 0
Z T Z T c p;m dT
Equation (9.20) introduces some problems in solution. The first is that dh m ¼ ,
T T
T 0 T 0
and this results in ln (0) when T ¼ T 0 . Fortunately these problems can be overcome by use of the