Page 96 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 96
4.7 AVAILABILITY BALANCE FOR A CLOSED SYSTEM 81
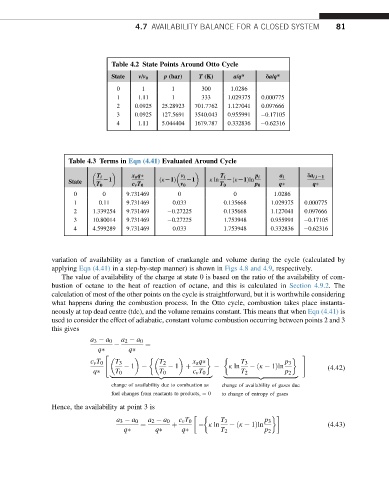
Table 4.2 State Points Around Otto Cycle
State v/v 0 p (bar) T (K) a/q* da/q*
0 1 1 300 1.0286
1 1.11 1 333 1.029375 0.000775
2 0.0925 25.28923 701.7762 1.127041 0.097666
3 0.0925 127.5691 3540.043 0.955991 0.17105
4 1.11 5.044404 1679.787 0.332836 0.62316
Table 4.3 Terms in Eqn (4.41) Evaluated Around Cycle
T i x a q v i T i p i a i da i;iL1
State L1 ðkL1Þ L1 k ln LðkL1Þln
T 0 c v T 0 v 0 T 0 p 0 q q
0 0 9.731469 0 0 1.0286
1 0.11 9.731469 0.033 0.135668 1.029375 0.000775
2 1.339254 9.731469 0.27225 0.135668 1.127041 0.097666
3 10.80014 9.731469 0.27225 1.753948 0.955991 0.17105
4 4.599289 9.731469 0.033 1.753948 0.332836 0.62316
variation of availability as a function of crankangle and volume during the cycle (calculated by
applying Eqn (4.41) in a step-by-step manner) is shown in Figs 4.8 and 4.9, respectively.
The value of availability of the charge at state 0 is based on the ratio of the availability of com-
bustion of octane to the heat of reaction of octane, and this is calculated in Section 4.9.2. The
calculation of most of the other points on the cycle is straightforward, but it is worthwhile considering
what happens during the combustion process. In the Otto cycle, combustion takes place instanta-
neously at top dead centre (tdc), and the volume remains constant. This means that when Eqn (4.41) is
used to consider the effect of adiabatic, constant volume combustion occurring between points 2 and 3
this gives
a 3 a 0 a 2 a 0
¼
q q
" #
c v T 0 T 3 T 2 x a q T 3 p 3
1 1 þ k ln ðk 1Þln (4.42)
q T 0 T 0 c v T 0 T 2 p 2
|fflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl{zfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl} |fflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl{zfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl}
change of availability due to combustion as change of availability of gases due
fuel changes from reactants to products; ¼ 0 to change of entropy of gases
Hence, the availability at point 3 is
a 3 a 0 a 2 a 0 c v T 0 T 3 p 3
¼ þ k ln ðk 1Þln (4.43)
q q q T 2 p 2