Page 439 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 439
408 Advanced Mine Ventilation
1.01ðTHCÞ CH 4
HR ¼ 1000 (24.10)
THC þ C
where THC is the sum of all hydrocarbons in ppm; CH 4 is the methane concentration
in ppm; C is a constant ¼ 0.01 ppm; HR ¼ 0 when no hydrocarbons are present;
HR ¼ 10 when only methane is present; Maximum HR ¼ 1010.
A limitation in Eq. (24.10) is that methane concentration must be above 20 ppm.
Interpretation of HR data is as follows:
When: 0 < HR < 50, normal conditions prevail.
50 < HR < 100, alleviated temperatures exist.
HR > 100, high temperature oxidation is in progress.
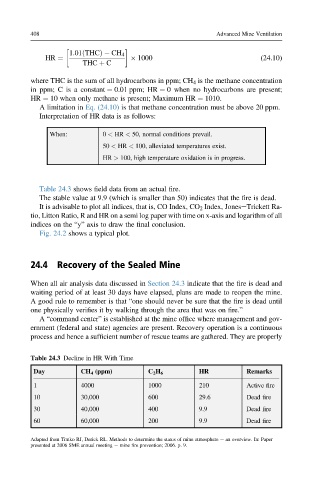
Table 24.3 shows field data from an actual fire.
The stable value at 9.9 (which is smaller than 50) indicates that the fire is dead.
It is advisable to plot all indices, that is, CO Index, CO 2 Index, JoneseTrickett Ra-
tio, Litton Ratio, R and HR on a semi log paper with time on x-axis and logarithm of all
indices on the “y” axis to draw the final conclusion.
Fig. 24.2 shows a typical plot.
24.4 Recovery of the Sealed Mine
When all air analysis data discussed in Section 24.3 indicate that the fire is dead and
waiting period of at least 30 days have elapsed, plans are made to reopen the mine.
A good rule to remember is that “one should never be sure that the fire is dead until
one physically verifies it by walking through the area that was on fire.”
A “command center” is established at the mine office where management and gov-
ernment (federal and state) agencies are present. Recovery operation is a continuous
process and hence a sufficient number of rescue teams are gathered. They are properly
Table 24.3 Decline in HR With Time
Day CH 4 (ppm) C 2 H 6 HR Remarks
1 4000 1000 210 Active fire
10 30,000 600 29.6 Dead fire
30 40,000 400 9.9 Dead fire
60 60,000 200 9.9 Dead fire
Adapted from Timko RJ, Derick RL. Methods to determine the status of mine atmosphere e an overview. In: Paper
presented at 2006 SME annual meeting e mine fire prevention; 2006. p. 9.