Page 121 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 121
Developing effective proximity detection systems for underground coal mines 105
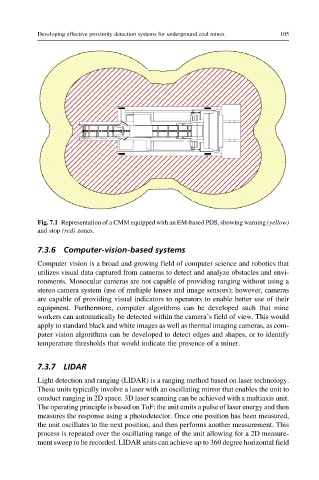
Fig. 7.1 Representation of a CMM equipped with an EM-based PDS, showing warning (yellow)
and stop (red) zones.
7.3.6 Computer-vision-based systems
Computer vision is a broad and growing field of computer science and robotics that
utilizes visual data captured from cameras to detect and analyze obstacles and envi-
ronments. Monocular cameras are not capable of providing ranging without using a
stereo camera system (use of multiple lenses and image sensors); however, cameras
are capable of providing visual indicators to operators to enable better use of their
equipment. Furthermore, computer algorithms can be developed such that mine
workers can automatically be detected within the camera’s field of view. This would
apply to standard black and white images as well as thermal imaging cameras, as com-
puter vision algorithms can be developed to detect edges and shapes, or to identify
temperature thresholds that would indicate the presence of a miner.
7.3.7 LIDAR
Light detection and ranging (LIDAR) is a ranging method based on laser technology.
These units typically involve a laser with an oscillating mirror that enables the unit to
conduct ranging in 2D space. 3D laser scanning can be achieved with a multiaxis unit.
The operating principle is based on ToF: the unit emits a pulse of laser energy and then
measures the response using a photodetector. Once one position has been measured,
the unit oscillates to the next position, and then performs another measurement. This
process is repeated over the oscillating range of the unit allowing for a 2D measure-
ment sweep to be recorded. LIDAR units can achieve up to 360 degree horizontal field