Page 307 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 307
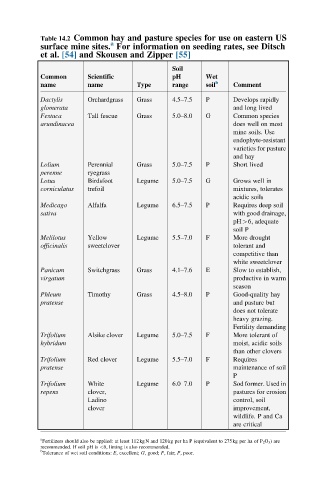
Table 14.2 Common hay and pasture species for use on eastern US
a
surface mine sites. For information on seeding rates, see Ditsch
et al. [54] and Skousen and Zipper [55]
Soil
Common Scientific pH Wet
name name Type range soil b Comment
Dactylis Orchardgrass Grass 4.5–7.5 P Develops rapidly
glomerata and long lived
Festuca Tall fescue Grass 5.0–8.0 G Common species
arundinacea does well on most
mine soils. Use
endophyte-resistant
varieties for pasture
and hay
Lolium Perennial Grass 5.0–7.5 P Short lived
perenne ryegrass
Lotus Birdsfoot Legume 5.0–7.5 G Grows well in
corniculatus trefoil mixtures, tolerates
acidic soils
Medicago Alfalfa Legume 6.5–7.5 P Requires deep soil
sativa with good drainage,
pH>6, adequate
soil P
Melilotus Yellow Legume 5.5–7.0 F More drought
officinalis sweetclover tolerant and
competitive than
white sweetclover
Panicum Switchgrass Grass 4.1–7.6 E Slow to establish,
virgatum productive in warm
season
Phleum Timothy Grass 4.5–8.0 P Good-quality hay
pratense and pasture but
does not tolerate
heavy grazing.
Fertility demanding
Trifolium Alsike clover Legume 5.0–7.5 F More tolerant of
hybridum moist, acidic soils
than other clovers
Trifolium Red clover Legume 5.5–7.0 F Requires
pratense maintenance of soil
P
Trifolium White Legume 6.0–7.0 P Sod former. Used in
repens clover, pastures for erosion
Ladino control, soil
clover improvement,
wildlife. P and Ca
are critical
a
Fertilizers should also be applied: at least 112kgN and 120kg per ha P (equivalent to 275kg per ha of P 2 O 5 ) are
recommended. If soil pH is <6, liming is also recommended.
b
Tolerance of wet soil conditions: E, excellent; G, good; F, fair; P, poor.