Page 266 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 266
Prospects and technological advancement of cellulosic bioethanol ecofuel production 229
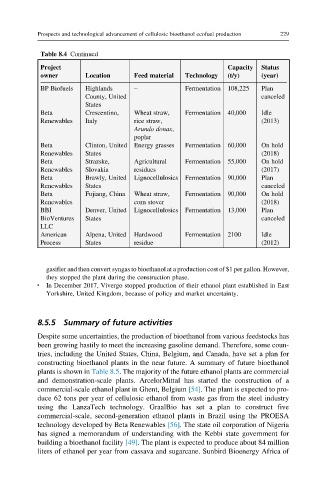
Table 8.4 Continued
Project Capacity Status
owner Location Feed material Technology (t/y) (year)
BP Biofuels Highlands – Fermentation 108,225 Plan
County, United canceled
States
Beta Crescentino, Wheat straw, Fermentation 40,000 Idle
Renewables Italy rice straw, (2013)
Arundo donax,
poplar
Beta Clinton, United Energy grasses Fermentation 60,000 On hold
Renewables States (2018)
Beta Strazske, Agricultural Fermentation 55,000 On hold
Renewables Slovakia residues (2017)
Beta Brawly, United Lignocellulosics Fermentation 90,000 Plan
Renewables States canceled
Beta Fujiang, China Wheat straw, Fermentation 90,000 On hold
Renewables corn stover (2018)
BBI Denver, United Lignocellulosics Fermentation 13,000 Plan
BioVentures States canceled
LLC
American Alpena, United Hardwood Fermentation 2100 Idle
Process States residue (2012)
gasifier and then convert syngas to bioethanol at a production cost of $1 per gallon. However,
they stopped the plant during the construction phase.
l In December 2017, Vivergo stopped production of their ethanol plant established in East
Yorkshire, United Kingdom, because of policy and market uncertainty.
8.5.5 Summary of future activities
Despite some uncertainties, the production of bioethanol from various feedstocks has
been growing hastily to meet the increasing gasoline demand. Therefore, some coun-
tries, including the United States, China, Belgium, and Canada, have set a plan for
constructing bioethanol plants in the near future. A summary of future bioethanol
plants is shown in Table 8.5. The majority of the future ethanol plants are commercial
and demonstration-scale plants. ArcelorMittal has started the construction of a
commercial-scale ethanol plant in Ghent, Belgium [54]. The plant is expected to pro-
duce 62 tons per year of cellulosic ethanol from waste gas from the steel industry
using the LanzaTech technology. GraalBio has set a plan to construct five
commercial-scale, second-generation ethanol plants in Brazil using the PROESA
technology developed by Beta Renewables [56]. The state oil corporation of Nigeria
has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Kebbi state government for
building a bioethanol facility [49]. The plant is expected to produce about 84 million
liters of ethanol per year from cassava and sugarcane. Sunbird Bioenergy Africa of