Page 214 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 214
Functionalisation of wool and silk fi bres using enzymes 195
laccase and peroxidase, are briefly reviewed in section 9.6. Finally, emerging
enzymatic activities, such as sulfydryl oxidase and protein disulfi de isomer-
ase, that are attracting the interest of scientists for their possible role in
protein fibre functionalisation, are mentioned.
9.2 Transglutaminases
9.2.1 Biological properties and biotechnological utility of
transglutaminases
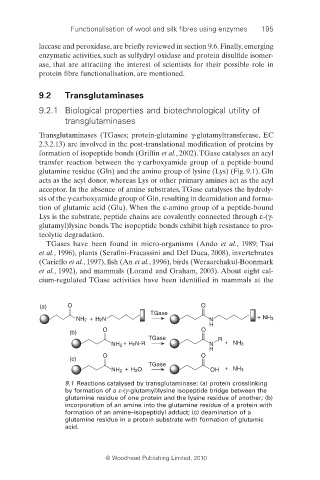
Transglutaminases (TGases; protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferase, EC
2.3.2.13) are involved in the post-translational modification of proteins by
formation of isopeptide bonds (Griffi n et al., 2002). TGase catalyses an acyl
transfer reaction between the γ-carboxyamide group of a peptide-bound
glutamine residue (Gln) and the amino group of lysine (Lys) (Fig. 9.1). Gln
acts as the acyl donor, whereas Lys or other primary amines act as the acyl
acceptor. In the absence of amine substrates, TGase catalyses the hydroly-
sis of the γ-carboxyamide group of Gln, resulting in deamidation and forma-
tion of glutamic acid (Glu). When the ε-amino group of a peptide-bound
Lys is the substrate, peptide chains are covalently connected through ε-(γ-
glutamyl)lysine bonds. The isopeptide bonds exhibit high resistance to pro-
teolytic degradation.
TGases have been found in micro-organisms (Ando et al., 1989; Tsai
et al., 1996), plants (Serafini-Fracassini and Del Duca, 2008), invertebrates
(Cariello et al., 1997), fi sh (An et al., 1996), birds (Weraarchakul-Boonmark
et al., 1992), and mammals (Lorand and Graham, 2003). About eight cal-
cium-regulated TGase activities have been identified in mammals at the
(a) O O
TGase
NH 2 + H 2N N + NH 3
H
O O
(b)
TGase R
+ H 2N-R N +
NH 2 NH 3
H
O O
(c)
TGase
+ H 2O OH + NH 3
NH 2
9.1 Reactions catalysed by transglutaminase: (a) protein crosslinking
by formation of a ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine isopeptide bridge between the
glutamine residue of one protein and the lysine residue of another; (b)
incorporation of an amine into the glutamine residue of a protein with
formation of an amine–isopeptidyl adduct; (c) deamination of a
glutamine residue in a protein substrate with formation of glutamic
acid.
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010