Page 84 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 84
Smart materials containing enzymes or enzyme substrates 63
O H
C N H
HO C N
H n
O
Enzymatic surface hydrolysis
NH 2
O
H N H
2
NH 2 HO C C OH N
H n
O
NH 2
NH GA GA (a)
Attachment
of enzymes
NH GA (b)
NH GA
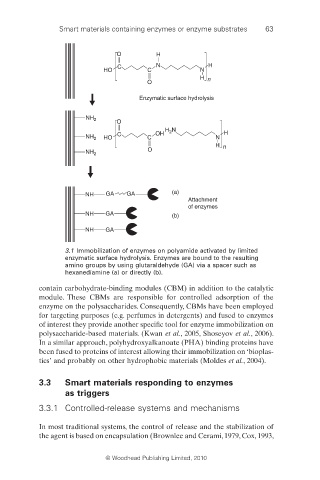
3.1 Immobilization of enzymes on polyamide activated by limited
enzymatic surface hydrolysis. Enzymes are bound to the resulting
amino groups by using glutaraldehyde (GA) via a spacer such as
hexanediamine (a) or directly (b).
contain carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM) in addition to the catalytic
module. These CBMs are responsible for controlled adsorption of the
enzyme on the polysaccharides. Consequently, CBMs have been employed
for targeting purposes (e.g. perfumes in detergents) and fused to enzymes
of interest they provide another specific tool for enzyme immobilization on
polysaccharide-based materials. (Kwan et al., 2005, Shoseyov et al., 2006).
In a similar approach, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) binding proteins have
been fused to proteins of interest allowing their immobilization on ‘bioplas-
tics’ and probably on other hydrophobic materials (Moldes et al., 2004).
3.3 Smart materials responding to enzymes
as triggers
3.3.1 Controlled-release systems and mechanisms
In most traditional systems, the control of release and the stabilization of
the agent is based on encapsulation (Brownlee and Cerami, 1979, Cox, 1993,
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010