Page 173 - Advances in bioenergy the sustainability challenge
P. 173
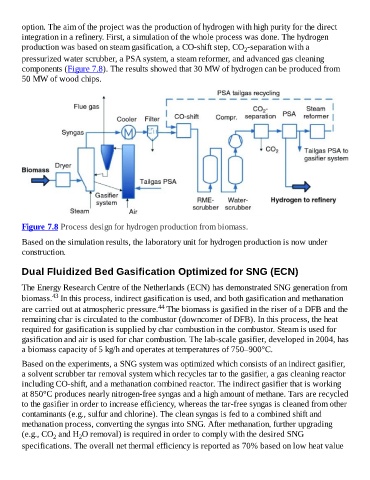
option. The aim of the project was the production of hydrogen with high purity for the direct
integration in a refinery. First, a simulation of the whole process was done. The hydrogen
production was based on steam gasification, a CO-shift step, CO -separation with a
2
pressurized water scrubber, a PSA system, a steam reformer, and advanced gas cleaning
components (Figure 7.8). The results showed that 30 MW of hydrogen can be produced from
50 MW of wood chips.
Figure 7.8 Process design for hydrogen production from biomass.
Based on the simulation results, the laboratory unit for hydrogen production is now under
construction.
Dual Fluidized Bed Gasification Optimized for SNG (ECN)
The Energy Research Centre of the Netherlands (ECN) has demonstrated SNG generation from
43
biomass. In this process, indirect gasification is used, and both gasification and methanation
44
are carried out at atmospheric pressure. The biomass is gasified in the riser of a DFB and the
remaining char is circulated to the combustor (downcomer of DFB). In this process, the heat
required for gasification is supplied by char combustion in the combustor. Steam is used for
gasification and air is used for char combustion. The lab-scale gasifier, developed in 2004, has
a biomass capacity of 5 kg/h and operates at temperatures of 750–900°C.
Based on the experiments, a SNG system was optimized which consists of an indirect gasifier,
a solvent scrubber tar removal system which recycles tar to the gasifier, a gas cleaning reactor
including CO-shift, and a methanation combined reactor. The indirect gasifier that is working
at 850°C produces nearly nitrogen-free syngas and a high amount of methane. Tars are recycled
to the gasifier in order to increase efficiency, whereas the tar-free syngas is cleaned from other
contaminants (e.g., sulfur and chlorine). The clean syngas is fed to a combined shift and
methanation process, converting the syngas into SNG. After methanation, further upgrading
(e.g., CO and H O removal) is required in order to comply with the desired SNG
2
2
specifications. The overall net thermal efficiency is reported as 70% based on low heat value