Page 131 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 131
Principles of flight dynamics 107
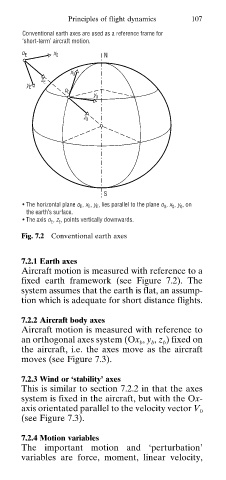
Conventional earth axes are used as a reference frame for
‘short-term’ aircraft motion.
o E x E N
x 0
z E
y E
o 0
y 0
z 0
S
• The horizontal plane o E , x E , y E , lies parallel to the plane o 0 , x 0 , y 0 , on
the earth’s surface.
• The axis o E , z E , points vertically downwards.
Fig. 7.2 Conventional earth axes
7.2.1 Earth axes
Aircraft motion is measured with reference to a
fixed earth framework (see Figure 7.2). The
system assumes that the earth is flat, an assump
tion which is adequate for short distance flights.
7.2.2 Aircraft body axes
Aircraft motion is measured with reference to
an orthogonal axes system (Ox b , y b , z b ) fixed on
the aircraft, i.e. the axes move as the aircraft
moves (see Figure 7.3).
7.2.3 Wind or ‘stability’ axes
This is similar to section 7.2.2 in that the axes
system is fixed in the aircraft, but with the Ox-
axis orientated parallel to the velocity vector V 0
(see Figure 7.3).
7.2.4 Motion variables
The important motion and ‘perturbation’
variables are force, moment, linear velocity,