Page 209 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 209
168 0.8 Aeronautical Engineer’s Data Book
Specific fuel consumption (sfc) lb/SHP hr 0.7
0.6
0.5
1950 60 70 80 90 2000
Year
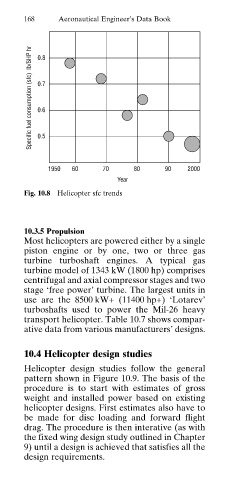
Fig. 10.8 Helicopter sfc trends
10.3.5 Propulsion
Most helicopters are powered either by a single
piston engine or by one, two or three gas
turbine turboshaft engines. A typical gas
turbine model of 1343 kW (1800 hp) comprises
centrifugal and axial compressor stages and two
stage ‘free power’ turbine. The largest units in
use are the 8500 kW+ (11400 hp+) ‘Lotarev’
turboshafts used to power the Mil-26 heavy
transport helicopter. Table 10.7 shows compar
ative data from various manufacturers’ designs.
10.4 Helicopter design studies
Helicopter design studies follow the general
pattern shown in Figure 10.9. The basis of the
procedure is to start with estimates of gross
weight and installed power based on existing
helicopter designs. First estimates also have to
be made for disc loading and forward flight
drag. The procedure is then interative (as with
the fixed wing design study outlined in Chapter
9) until a design is achieved that satisfies all the
design requirements.