Page 196 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 196
04_chap_Wang.qxd 05/05/2004 1:15 pm Page 175
Electrostatistic Precipitation 175
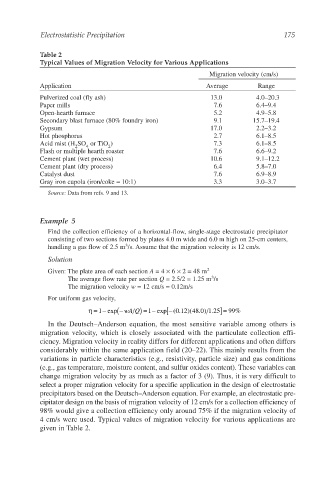
Table 2
Typical Values of Migration Velocity for Various Applications
Migration velocity (cm/s)
Application Average Range
Pulverized coal (fly ash) 13.0 4.0–20.3
Paper mills 7.6 6.4–9.4
Open-hearth furnace 5.2 4.9–5.8
Secondary blast furnace (80% foundry iron) 9.1 15.7–19.4
Gypsum 17.0 2.2–3.2
Hot phosphorus 2.7 6.1–8.5
Acid mist (H SO or TiO ) 7.3 6.1–8.5
2 4 2
Flash or multiple hearth roaster 7.6 6.6–9.2
Cement plant (wet process) 10.6 9.1–12.2
Cement plant (dry process) 6.4 5.8–7.0
Catalyst dust 7.6 6.9–8.9
Gray iron cupola (iron/coke = 10:1) 3.3 3.0–3.7
Source: Data from refs. 9 and 13.
Example 5
Find the collection efficiency of a horizontal-flow, single-stage electrostatic precipitator
consisting of two sections formed by plates 4.0 m wide and 6.0 m high on 25-cm centers,
3
handling a gas flow of 2.5 m /s. Assume that the migration velocity is 12 cm/s.
Solution
Given: The plate area of each section A = 4 × 6 × 2 = 48 m 2
The average flow rate per section Q = 2.5/2 = 1.25 m /s
3
The migration velocity w = 12 cm/s = 0.12m/s
For uniform gas velocity,
− [
η= − exp − ( wA Q ) =−1 exp ( 0 12 48 0 1 25 ] = 99%
1
.
.
)(
)
.
In the Deutsch–Anderson equation, the most sensitive variable among others is
migration velocity, which is closely associated with the particulate collection effi-
ciency. Migration velocity in reality differs for different applications and often differs
considerably within the same application field (20–22). This mainly results from the
variations in particle characteristics (e.g., resistivity, particle size) and gas conditions
(e.g., gas temperature, moisture content, and sulfur oxides content). These variables can
change migration velocity by as much as a factor of 3 (9). Thus, it is very difficult to
select a proper migration velocity for a specific application in the design of electrostatic
precipitators based on the Deutsch–Anderson equation. For example, an electrostatic pre-
cipitator design on the basis of migration velocity of 12 cm/s for a collection efficiency of
98% would give a collection efficiency only around 75% if the migration velocity of
4 cm/s were used. Typical values of migration velocity for various applications are
given in Table 2.