Page 476 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 476
12_ch_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 5:26 pm Page 448
448 Lawerence K. Wang et al.
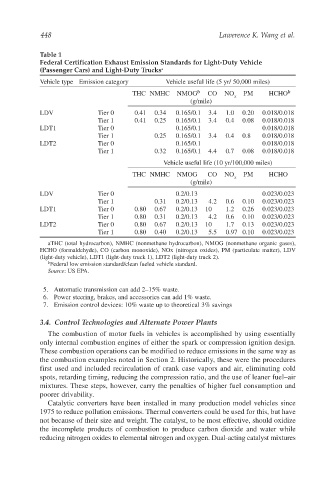
Table 1
Federal Certification Exhaust Emission Standards for Light-Duty Vehicle
(Passenger Cars) and Light-Duty Trucks a
Vehicle type Emission category Vehicle useful life (5 yr/ 50,000 miles)
THC NMHC NMOG b CO NO PM HCHO b
x
(g/mile)
LDV Tier 0 0.41 0.34 0.165/0.1 3.4 1.0 0.20 0.018/0.018
Tier 1 0.41 0.25 0.165/0.1 3.4 0.4 0.08 0.018/0.018
LDT1 Tier 0 0.165/0.1 0.018/0.018
Tier 1 0.25 0.165/0.1 3.4 0.4 0.8 0.018/0.018
LDT2 Tier 0 0.165/0.1 0.018/0.018
Tier 1 0.32 0.165/0.1 4.4 0.7 0.08 0.018/0.018
Vehicle useful life (10 yr/100,000 miles)
THC NMHC NMOG CO NO PM HCHO
x
(g/mile)
LDV Tier 0 0.2/0.13 0.023/0.023
Tier 1 0.31 0.2/0.13 4.2 0.6 0.10 0.023/0.023
LDT1 Tier 0 0.80 0.67 0.2/0.13 10 1.2 0.26 0.023/0.023
Tier 1 0.80 0.31 0.2/0.13 4.2 0.6 0.10 0.023/0.023
LDT2 Tier 0 0.80 0.67 0.2/0.13 10 1.7 0.13 0.023/0.023
Tier 1 0.80 0.40 0.2/0.13 5.5 0.97 0.10 0.023/0.023
aTHC (total hydrocarbon), NMHC (nonmethane hydrocarbon), NMOG (nonmethane organic gases),
HCHO (formaldehyde), CO (carbon monoxide), NOx (nitrogen oxides), PM (particulate matter), LDV
(light-duty vehicle), LDT1 (light-duty truck 1), LDT2 (light-duty truck 2).
b Federal low emission standard/clean fueled vehicle standard.
Source: US EPA.
5. Automatic transmission can add 2–15% waste.
6. Power steering, brakes, and accessories can add 1% waste.
7. Emission control devices: 10% waste up to theoretical 3% savings
3.4. Control Technologies and Alternate Power Plants
The combustion of motor fuels in vehicles is accomplished by using essentially
only internal combustion engines of either the spark or compression ignition design.
These combustion operations can be modified to reduce emissions in the same way as
the combustion examples noted in Section 2. Historically, these were the procedures
first used and included recirculation of crank case vapors and air, eliminating cold
spots, retarding timing, reducing the compression ratio, and the use of leaner fuel–air
mixtures. These steps, however, carry the penalties of higher fuel consumption and
poorer drivability.
Catalytic converters have been installed in many production model vehicles since
1975 to reduce pollution emissions. Thermal converters could be used for this, but have
not because of their size and weight. The catalyst, to be most effective, should oxidize
the incomplete products of combustion to produce carbon dioxide and water while
reducing nitrogen oxides to elemental nitrogen and oxygen. Dual-acting catalyst mixtures