Page 54 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 54
01_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 11:46 am Page 34
34 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
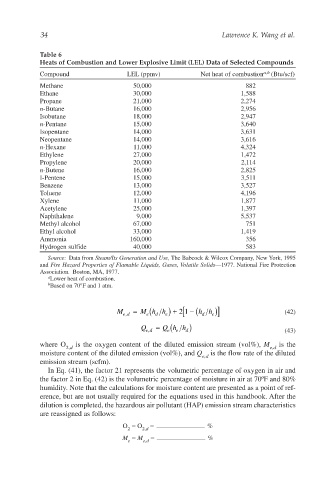
Table 6
Heats of Combustion and Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) Data of Selected Compounds
Compound LEL (ppmv) Net heat of combustion a,b (Btu/scf)
Methane 50,000 882
Ethane 30,000 1,588
Propane 21,000 2,274
n-Butane 16,000 2,956
Isobutane 18,000 2,947
n-Pentane 15,000 3,640
Isopentane 14,000 3,631
Neopentane 14,000 3,616
n-Hexane 11,000 4,324
Ethylene 27,000 1,472
Propylene 20,000 2,114
n-Butene 16,000 2,825
I-Pentene 15,000 3,511
Benzene 13,000 3,527
Toluene 12,000 4,196
Xylene 11,000 1,877
Acetylene 25,000 1,397
Naphthalene 9,000 5,537
Methyl alcohol 67,000 751
Ethyl alcohol 33,000 1,419
Ammonia 160,000 356
Hydrogen sulfide 40,000 583
Source: Data from Steam/Its Generation and Use, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, New York, 1995
and Fire Hazard Properties of Flamable Liquids, Gases, Volatile Solids—1977. National Fire Protection
Association. Boston, MA, 1977.
a Lower heat of combustion.
b Based on 70°F and 1 atm.
[
d (
e(
M ed = M h h ) + 21 − hh )] (42)
,
e
d
e
e(
Q = Q h h )
ed e d (43)
,
where O is the oxygen content of the diluted emission stream (vol%), M is the
2,d e,d
moisture content of the diluted emission (vol%), and Q is the flow rate of the diluted
e,d
emission stream (scfm).
In Eq. (41), the factor 21 represents the volumetric percentage of oxygen in air and
the factor 2 in Eq. (42) is the volumetric percentage of moisture in air at 70ºF and 80%
humidity. Note that the calculations for moisture content are presented as a point of ref-
erence, but are not usually required for the equations used in this handbook. After the
dilution is completed, the hazardous air pollutant (HAP) emission stream characteristics
are reassigned as follows:
O = O = %
2 2,d
M = M = %
e e,d